50 Years of the Chevrolet Corvette

Here’s what we’re going to do. We’re going to show you every Corvette from 1968 until now, and we’re going to tell you all about it. And you are going to love it…because it’s all about the Corvette and you love the Corvette! Just like us. The transformation of this vehicle over the last 50+ years is amazing (and not always good-looking, if we may so so ourselves).
So without further ado, let’s dial back the clocks 50 years and check in on the Vette!
1968

The C3 was the third generation of the Chevrolet’s Corvette sports car. With the popularity of the previous generation’s Sting Ray and the growing number of muscle cars on the market, Chevy needed to launch something that exceeded expectations. Chevrolet’s engineering director Frank Winchell and designers Zora Duntov and Billy Mitchell got to work on the new concept. Mitchell eventually hired Larry Shinoda to help. They came up with the Mako Shark II design with a new body and interior plus scraped the mid-engine format present in the C2. After a one year delay, the C3 debuted in 1968. The 1968 Corvette was available in either a convertible or coupe model. The fiberglass body featured a slim midsection, swept rear fenders, and a sharp front end.
It was not as intensely stylized as the Shark II concept. The C3 continued using the engines and chassis components from the C2.
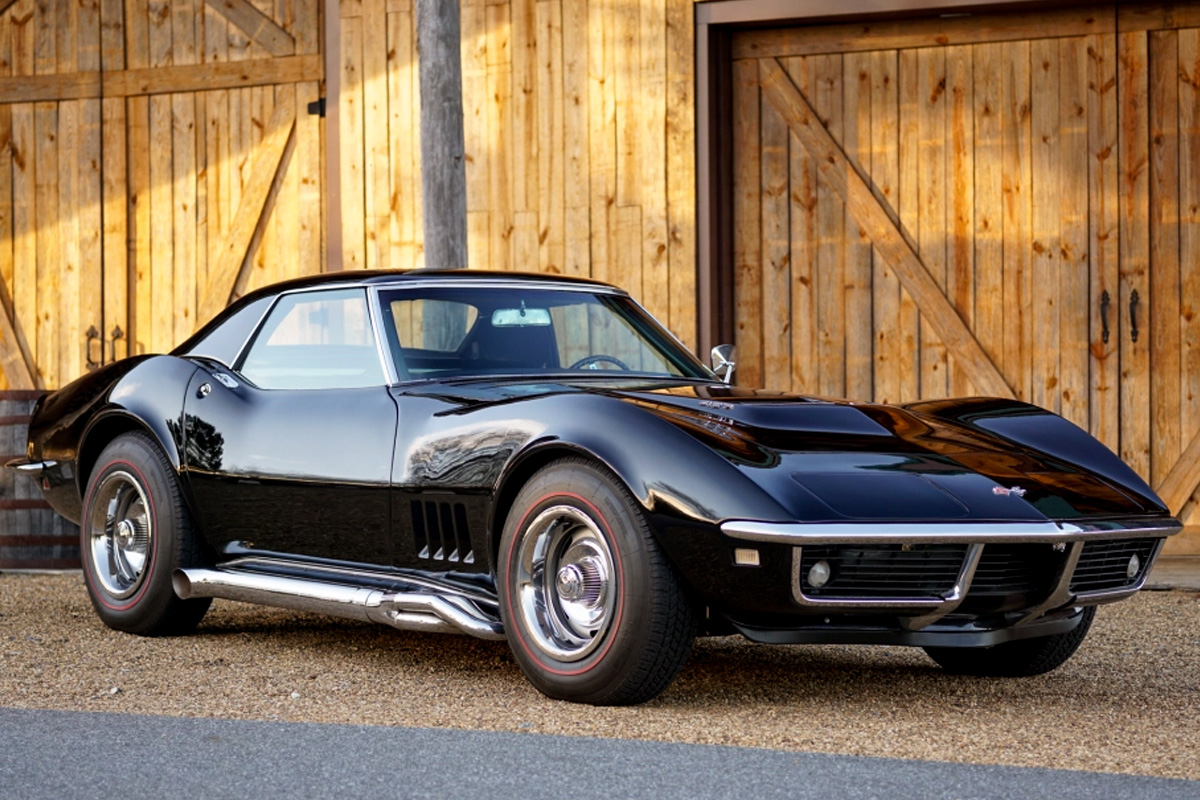
1969

Going from the 1968 to 1969 Corvette model, nothing changed much. The small-block engine displacement grew from 327 cu in to 350 cu in, and steering was decreased from 16 to 15 inches. Cosmetically the front grilles were now all black, and the “Sting Ray” designation was changed to “Stingray” as one word on the nameplates. As for the Vette in the picture, Jim Rathmann Indy 500 winner and Florida Chevrolet dealer offered the uniquely painted vehicle to astronauts for one dollar per year. Alan Bean, Pete Conrad, and Dick Gordon took Rathmann up on his offer. They formulated the paint scheme. Bean’s car is the only one of the three’s cars that is still around.
1970

The 1970 Corvette included fender flares that fit in the body contours, egg-crate grills, redesigned seats, and interiors. The most significant addition was the “LT-1” option, which included a 350 cu in small-block V8 Engine, which offered 370 horsepower plus “LT-1” decals. These versions did not come with air conditioning. Additionally, with LT-1 vehicles, you could purchase the ZR1 package, which included racing suspension, brakes, stabilizer bars, etc. Chevrolet only manufactured 17, 316 models that year.
1971
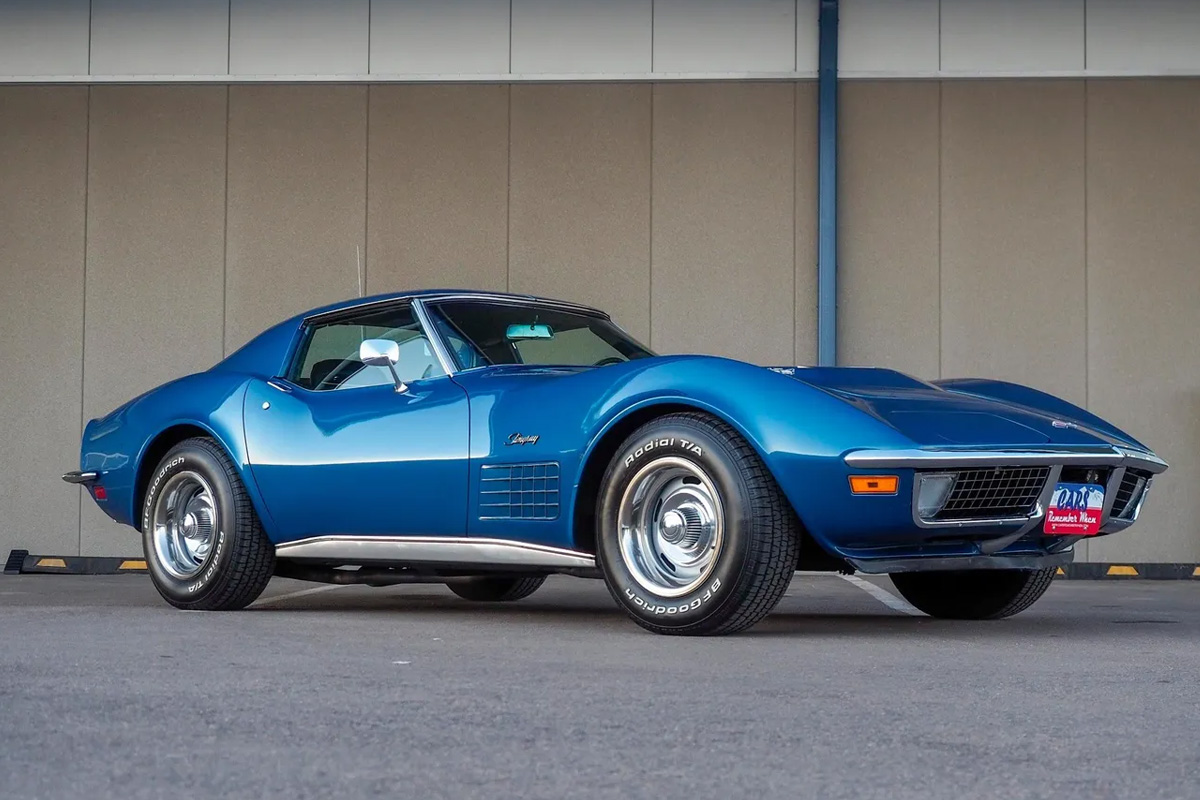

Chevrolet barely made any changes for the 1971 Corvette. It is one of the least changed models in the company’s history. According to Cor Sport, what happened was the 1969 model year ran over by two months, drastically shorting the 1970 Corvette production by four months. As a result, Chevrolet treated the 1971 line as an extension of the 1970 model. On the plus side, the manufacturers put air conditioning in most of the cars. Also, engines were detuned. The outcome lowered compression to withstand lower octane fuel. Lastly, this is the only year to offer a ZR2 option, which came with a 454 cu in LS6 Engine.
1972
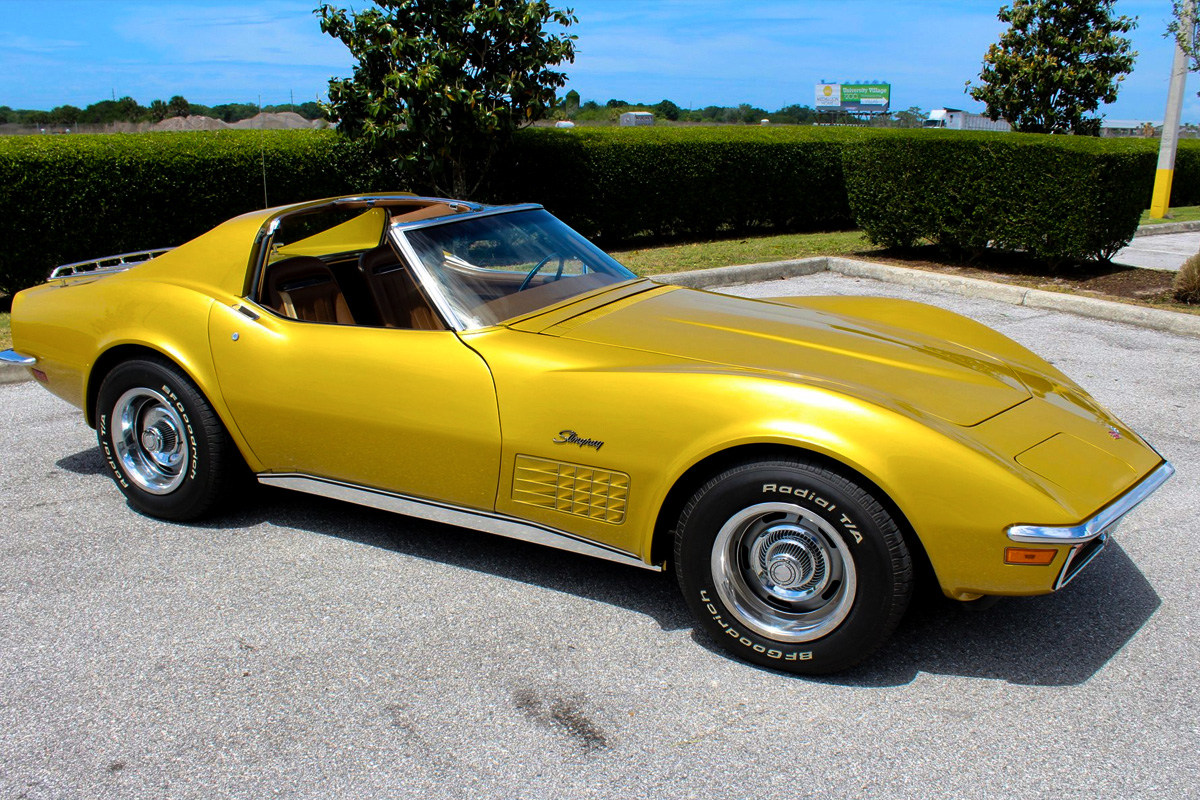

The 1972 Corvette also went largely unchanged cosmetically or mechanically. In fact, this model year, the Corvette lost several features, including the ZR2 option. Only three engines were available, and they all lost power due to emission-lowering regulations that year. GM now conformed to the SAE “net” measure for engine outputs. If you were in California, your choices were even more limited, with Chevrolet omitting certain builds due to state laws, including the LS5. On the plus side, the vehicles came equipped with anti-theft alarm systems, and it was the last year Chevy included chrome bumpers in the front and rear.
1973
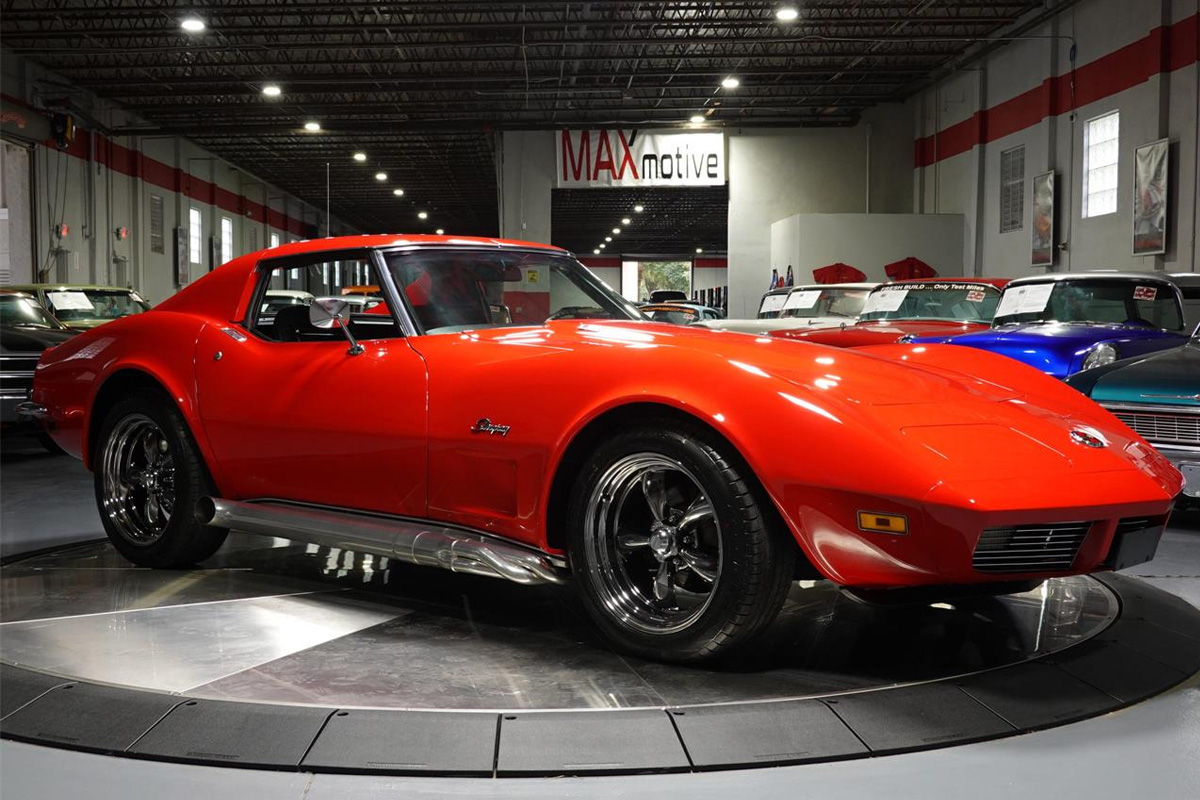

The Corvette had been on the market for nearly two decades, proving its longevity. What did Chevrolet do for the vehicle’s twentieth anniversary? A slight redesign. This model year marked the first significant visual and performance changes since the C3’s introduction. Chevrolet stated in an advertisement, “We gave it radials, a quieter ride, guard beams, and a nose job.” The vehicle included radial tires and a urethane nose, which was about two inches longer than the previous model. Also, GM abandoned the chrome bumper. GM included steel “birdcage” in the car for safety purposes. This year was definitely a step up.
1974
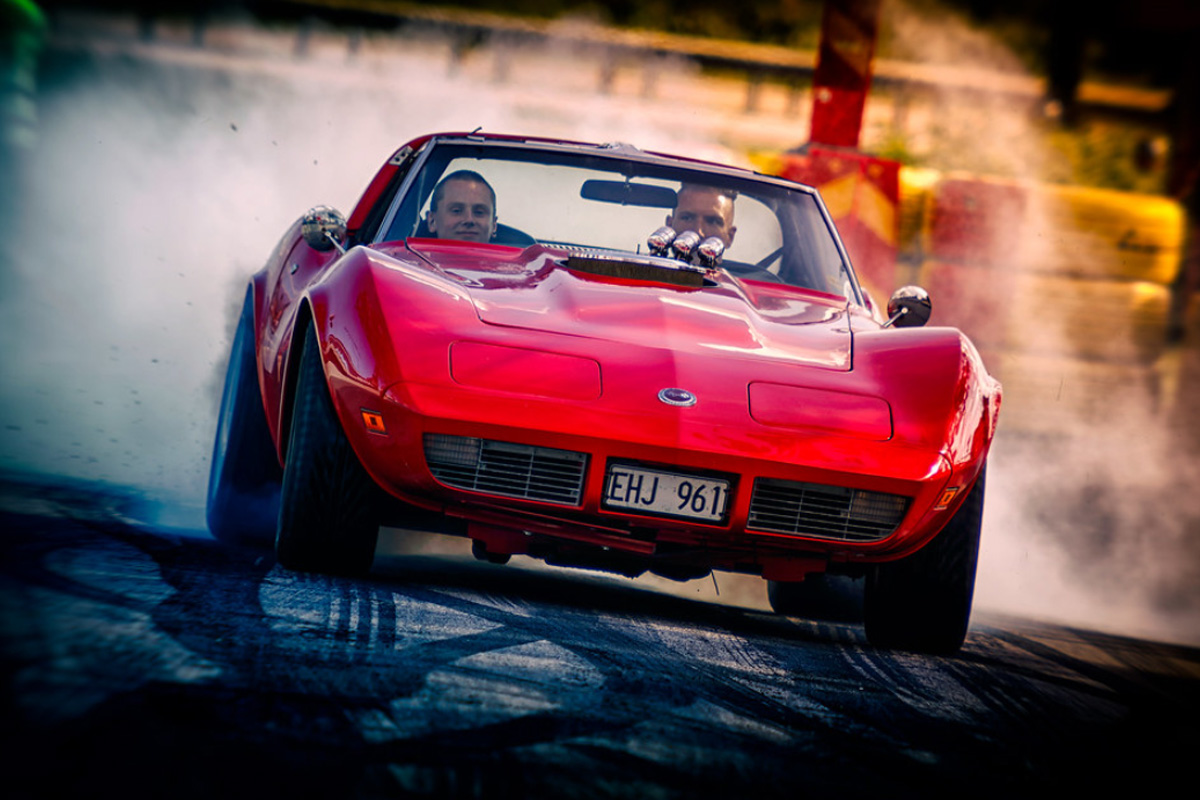

The 1974 Corvette included a new rear bumper system, including a unique urethane plastic skin covering the license plate holder and rests for the round taillights. The designers separated these two sections with a vertical center seam. This particular setup makes it easy to identify the model year. Other new additions included an increase in the RPO ZQ3 engine’s output, a tougher Turbo Hydra-Matic (put in the majority of Vettes), and a redesigned radiator. Resonators were also included in the dual exhaust system making the interior even quieter. Sadly, ’74 was the last year Chevrolet included the option for a big-block 454 cu in V-8 Engine. In 1986, Hot Rod Magazine placed the 1973-74 Corvette LS4 454 in their “10 most collectible muscle cars.”
1975
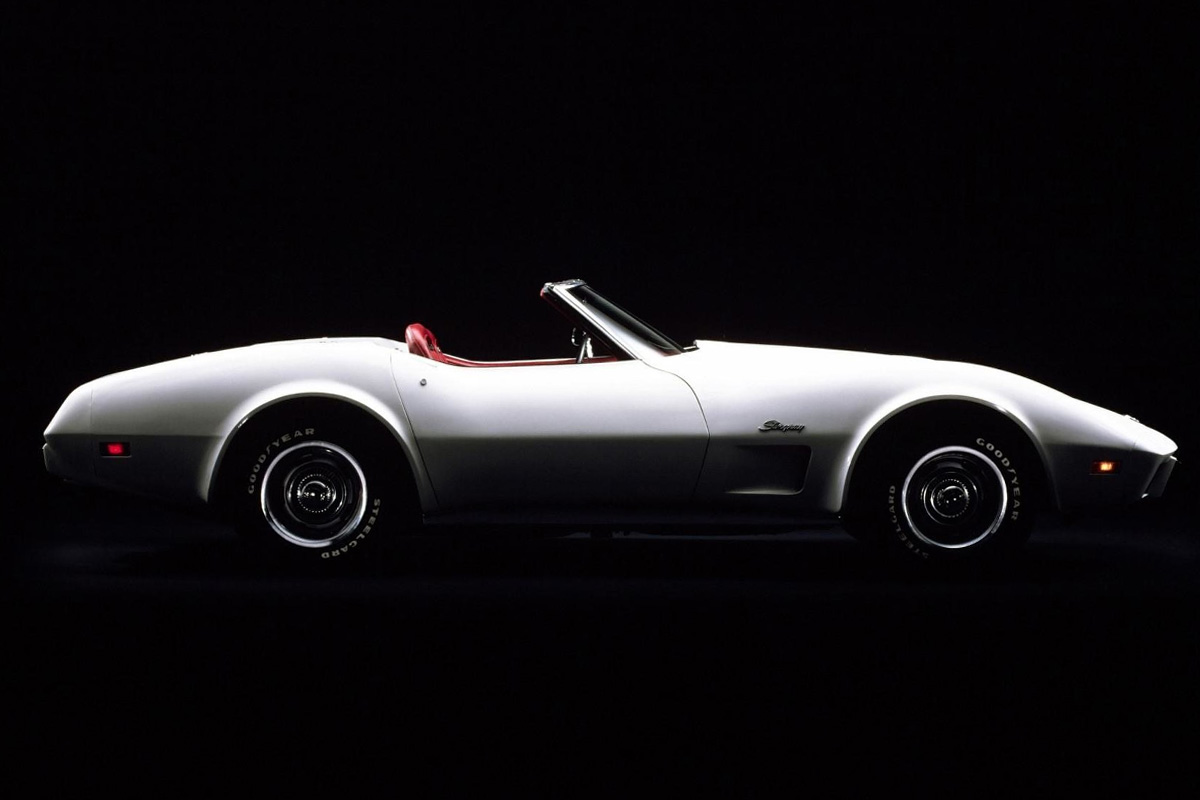

Cosmetically the 1975 Corvette resembled the 1974 model. The biggest difference is the rear. The 1975 model included front and rear bumper pads. The urethane plastic bumper was molded as a single piece rather than two featured on the 1974 Corvette. Chevrolet included the federally mandated catalytic converter with the “unleaded fuel only” warnings and extended service intervals and electronic ignition. They advertised the car as the most “efficient Corvette.” The base engine only delivered 165 hp while the L-82 produced 205 hp (45 hp lower than its predecessor). Finally, this was the last year of the C3 to include a convertible type. The main reason for the subsequent omission was diminishing sales and proposed government legislation threatening open cars. The car was a commercial success.
1976
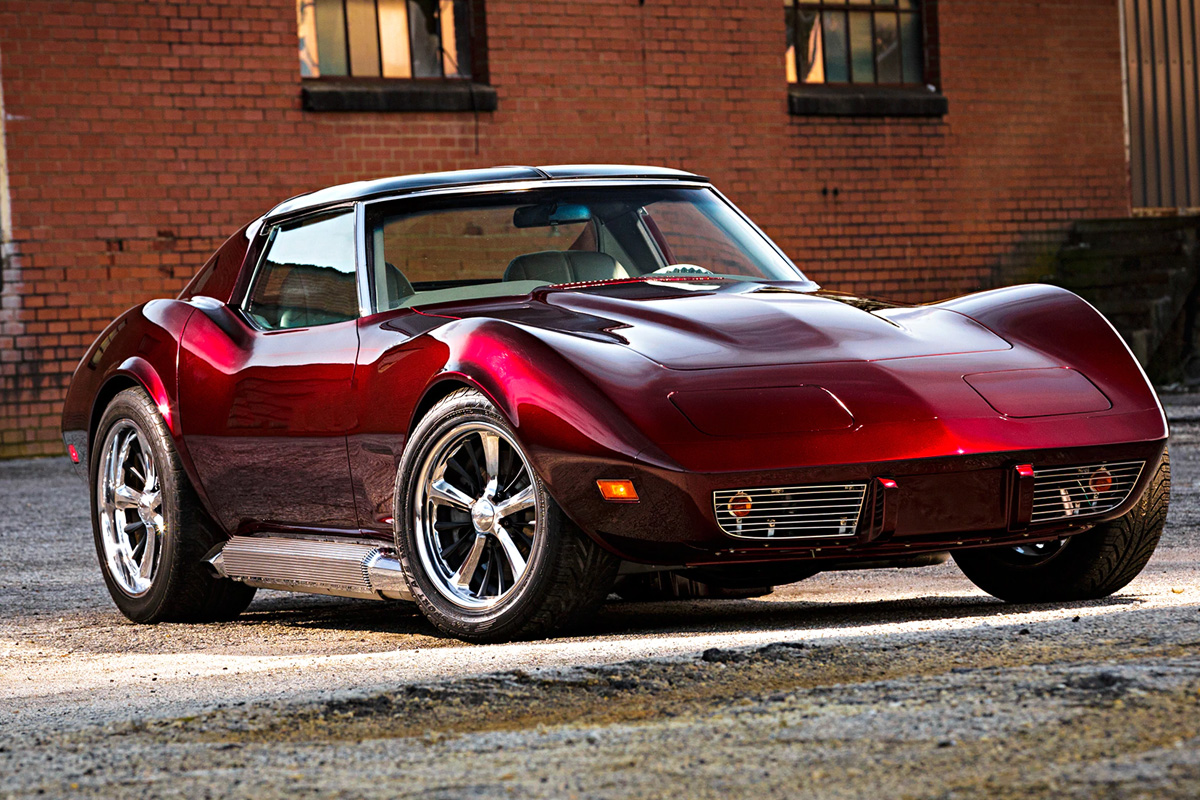

The 1976 Corvette included steel panels covering the catalytic converter. Chevrolet removed the cowl cap replacing it with an air cleaner duct over the radiator. They also introduced two bumper/fascia assemblies for the rear. Additionally, all the engine options performed slightly better than the preceding year. The most significant change was the re-introduction of aluminum wheels last seen in 1973. Despite an economic recession, a raised price, and no convertible edition, the 1976 Corvette set new sale records.
1977
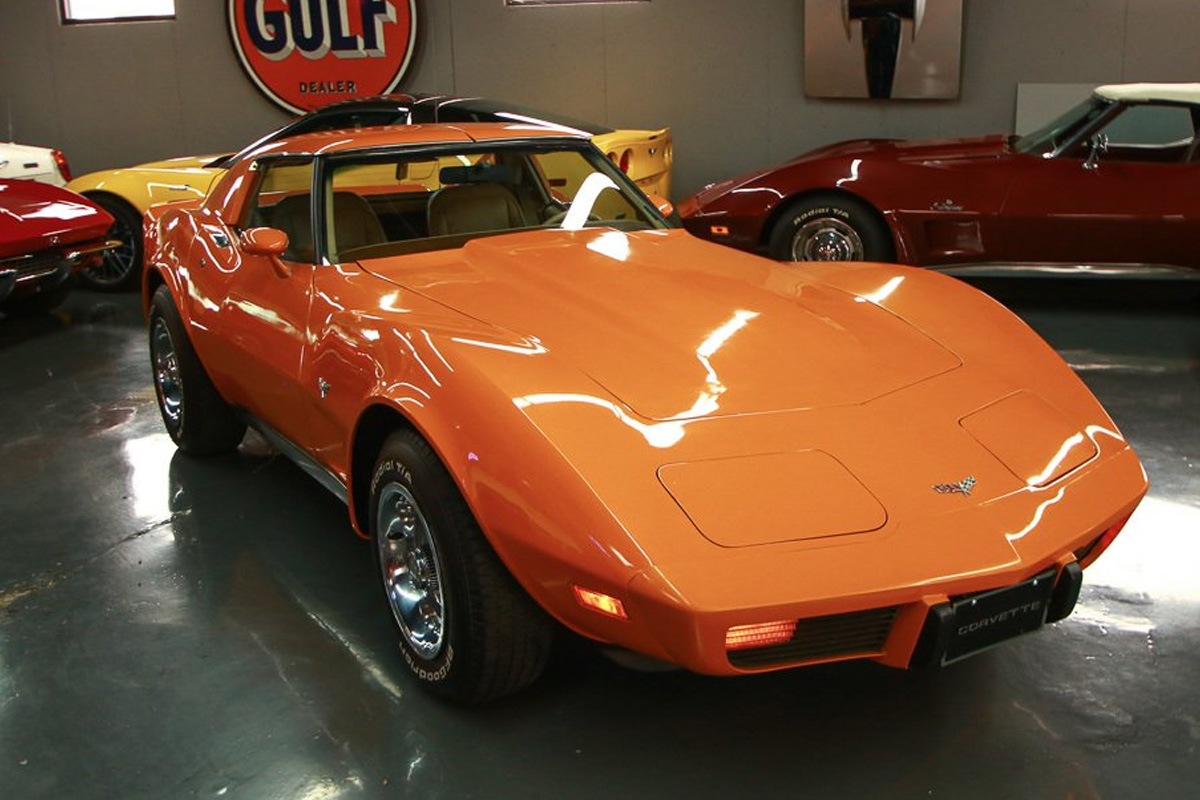

1977 marked a big year for Chevrolet’s sports car. They manufactured their 500,000th Corvette with a white coupe driven off the line by Chevrolet General Manager, Robert Lund, on March 15. As for the car itself, it did not see too much modification from the 1976 model. Inside, the steering wheel was moved 2 inches closer to the dashboard. Speaking of steering wheels, due to criticism, Chevrolet included a new three-spoke leather-wrapped unit. It also came fitted with an optional tilt-telescopic steering column. The wheel was well received and featured on the front of the vehicle’s brochure. This year, cruise control also became an available option for the first time with cars that used an automatic transmission. Once again, proving the vehicle’s popularity, sales for the 1977 model were outstanding, setting a record at 49,213 units sold.
1978
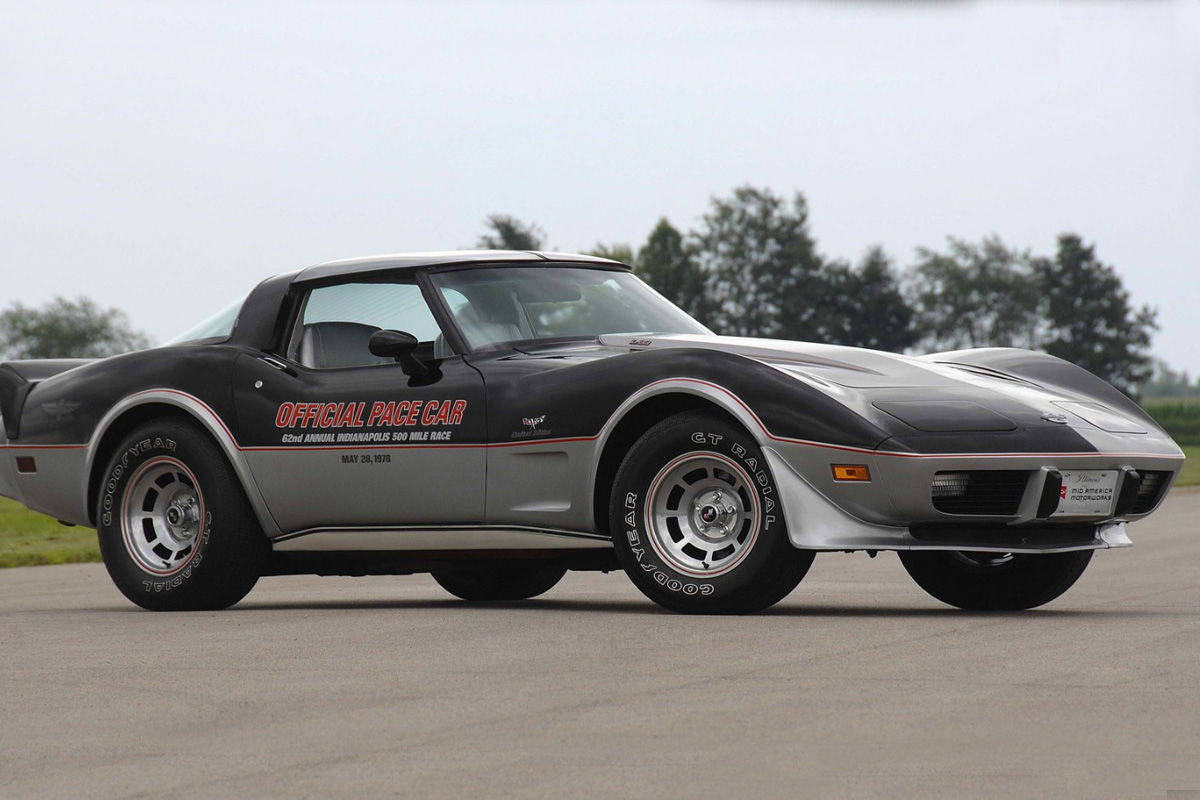

In 1978, Corvette was celebrating its twenty-fifth anniversary. For the model this year, the biggest change was the fastback rear window. The styling gave the aging C3 Corvette a new look. The fastback helped with aerodynamics and made more luggage space behind the seats available. Along with the fastback, the tachometer and speedometer saw an update, and the interior door panels got a redesign. Mechanically, this Corvette received a larger fuel tank with 24 gallons versus the ’77 mode’s 17 gallons. For the 1978 model year, this Corvette received two special editions: the Silver Anniversary model and the 6502 Indy-500 Pace Car replica edition. The Pace Car edition is one of the most popular C3 Corvettes Chevrolet ever designed.
1979

Chevrolet put out a record number of 53,807 Corvettes in 1979. It was the highest number of units the company manufactured in the vehicle’s 26-year run. Most 1979, Corvettes included telescopic steering columns, power windows, and air conditioning for their base models, and by the end of the year, it had become the standard. As a result, the cost went well past $10,000 near the end production. Also introduced this year were tungsten-halogen headlights and a new “open flow” muffler design,” which increased all engines horsepower by 5. Additionally, Chevrolet brought over features from the 1978 Pace Car replica, most notably the “high back” seat style, which became a standard for the car.
1980

According to Cor Sport, CAFE (Corporate Average Fuel Economy) regulations forced Chevrolet to find a way to trim weight on their cars. In response, the 1980 Corvette had lower density roof panels and aluminum Dana 44 IRS (Independent Rear Suspension).
Chrome was also used minimally. Along with weight, engineers tried to get better gas mileage results. They focused their efforts on gas mileage, which they improved by reworking the optional front and rear spoilers as well as bringing back the front grill. Lastly, overall emission control lowered the bhp for all engines.
1981

The 1981 Corvette model remained mostly unchanged. The most prominent inclusion was the standard 350 cu in V-8 Engine labeled the L81, which produced 190 hp. This Engine was certified in every state, including California, and included manual and automatic transmission. Another edition Chevrolet provided was a fiberglass rear spring and Computer Command Control (CCC). Lastly, production moved from St. Louis, Missouri to Bowling Green, Kentucky, in the middle of the year.
1982

In 1982, the C3 generation was coming to a close. The 1982 Corvette included the “Cross-Fire Injection” fuel delivery system. The TBI (Throttle Body Fuel Injection) used two throttle bodies and Chevrolet’s Computer control system. The Engine also saw a bit of a boost and was linked to a new four-speed transmission producing 200 hp. Chevrolet was aware this was the last C3 and offered a Collector’s Edition with silver-beige paint and different patterned wheels.
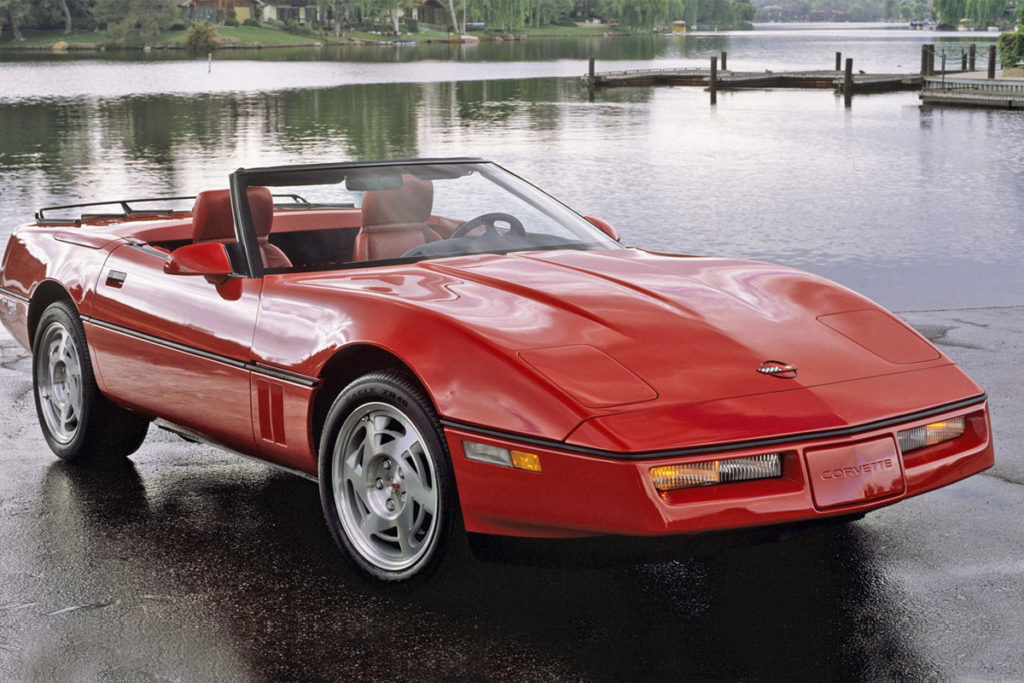
1984
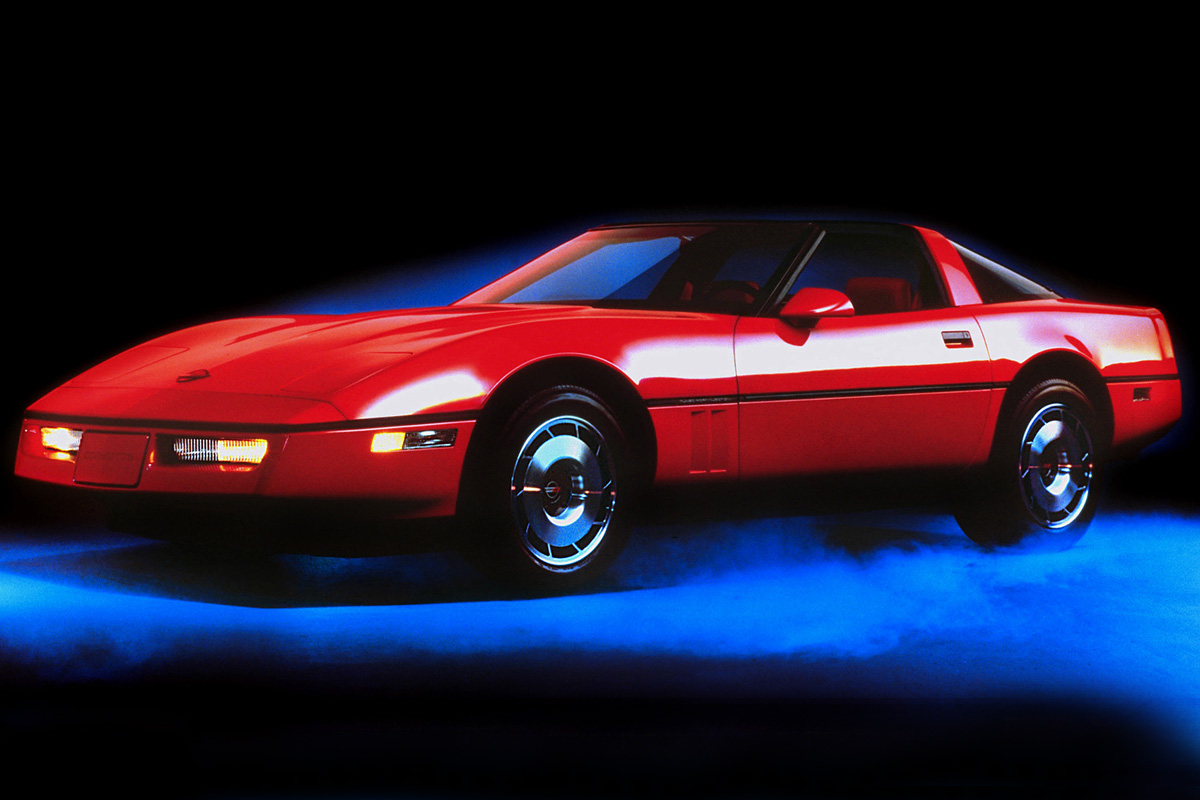

After a year’s absence, Chevrolet returned with the next generation of Corvette. The company unveiled the C4 on March 1983. Dave McLellan and his team designed the vehicle. It departed in many ways from the C3 with a new chassis, new styling, and no grill. Still, it looked undeniably like a Corvette with the round taillights, pop-up headlights, and wrap-around rear window. New to the C4 was a glass hatchback, rear bumper/panels made from molding plastics, and an electronic dashboard that displayed graphics for fuel level and other functions. It also included the same L83 Engine from the 1982 model. The first C4 models hit the market in January 1984.
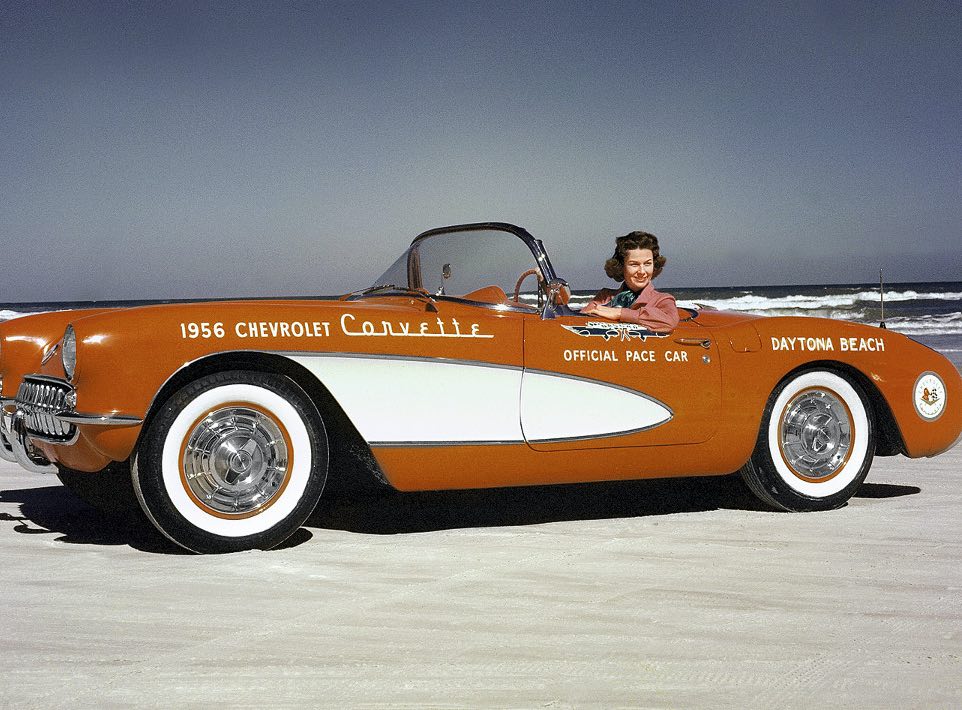
What do you think of this model compared to the absolute classic 1957 model seen below?

1985
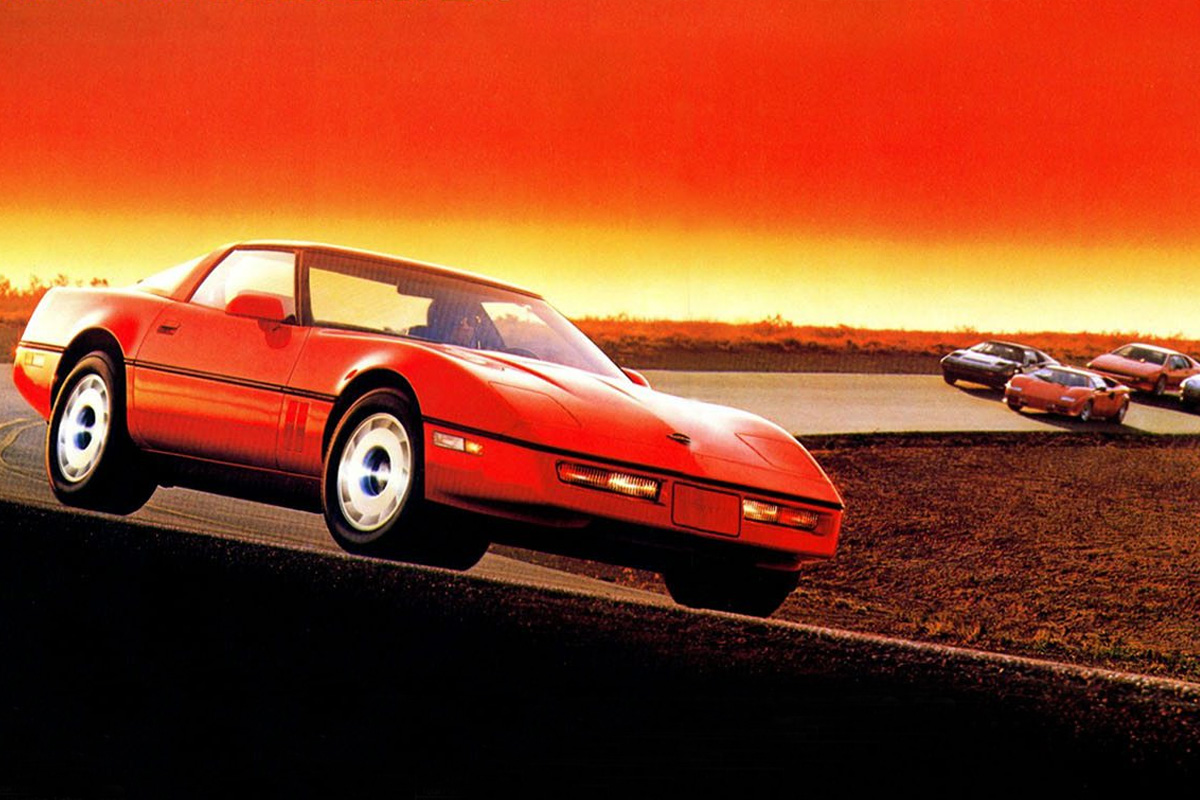
At long last, Chevrolet abandoned the Corvette’s Cross-Fire Injection system. They replaced it with the “Tuned Port Injection” fuel delivery system with mixed results. Another addition to the 1985 Corvette model was a more reliable and fuel-efficient L98 Engine. With the Z51 package, Chevrolet included suspension changes. This year, the price increased but noted as an improvement over the 1984 model. The criticism levied at the car stated the short rack steering was too quick.
1986
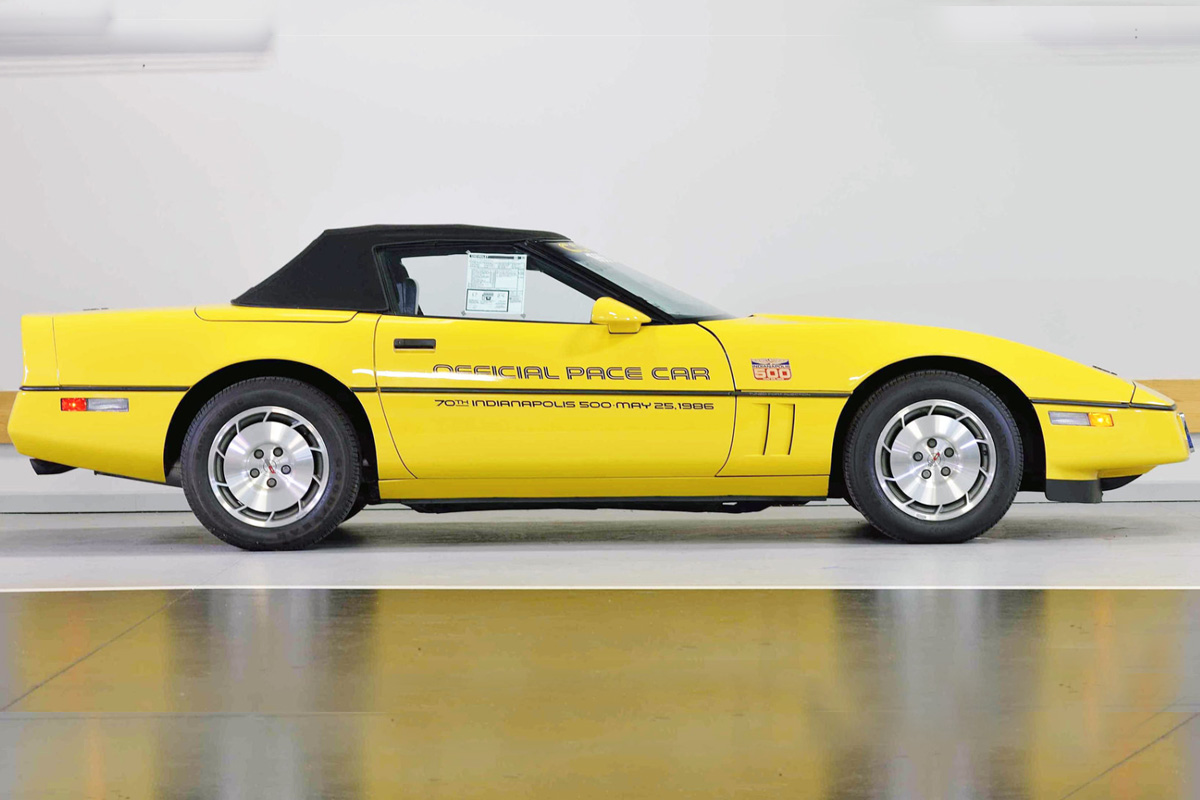

The 1986 Corvette included many new additions such as third brake light and electronic climate control. It also had a Vehicle Anti-Theft System (VATS), which complemented the existing alarm system. It was so effective that Corvette theft went down from 7% to less than 1%, and some insurance companies even reduced their rates for Corvettes that included the system. Also new was the Vette’s Antilock brakes (ABS), which stopped the wheel from locking up in severe braking circumstances and prevent loss of control of the vehicle. Chevrolet brought back the convertible, and 7,315 units had Indy 500 pace care console id plaque along with the standard model.
1987
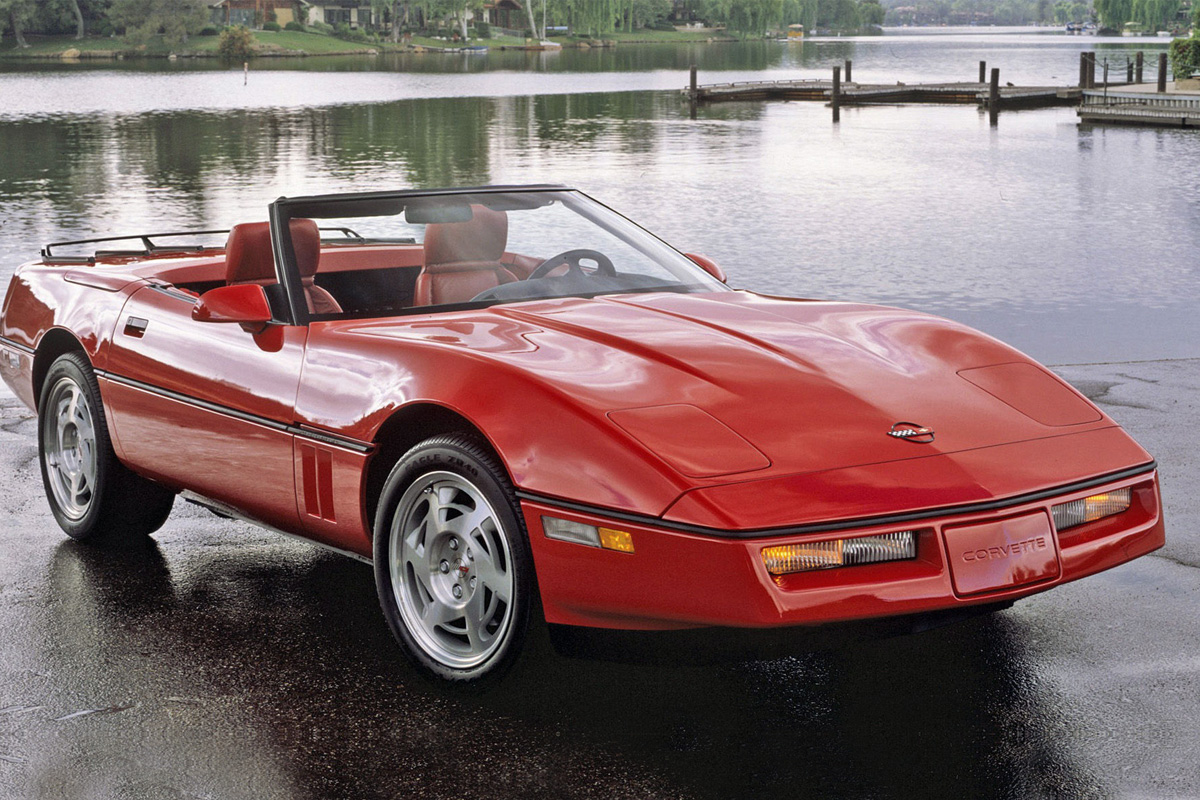

For 1987 Corvette, Chevrolet wanted to decrease engine friction while also refining the vehicle’s fuel economy and engine performance. This year’s model included hydraulic lifters, which added ten horsepower raising the Engine’s rating to 240hp. Along with horsepower, the Engine had better torque. A Callaway Twin-Turbo Engine package could be purchased from participating dealerships with a GM warranty, but it was not a factory option. Cosmetically, the 1987 Corvette looked mostly identical to previous C4 models minus a change in wheels.
1988
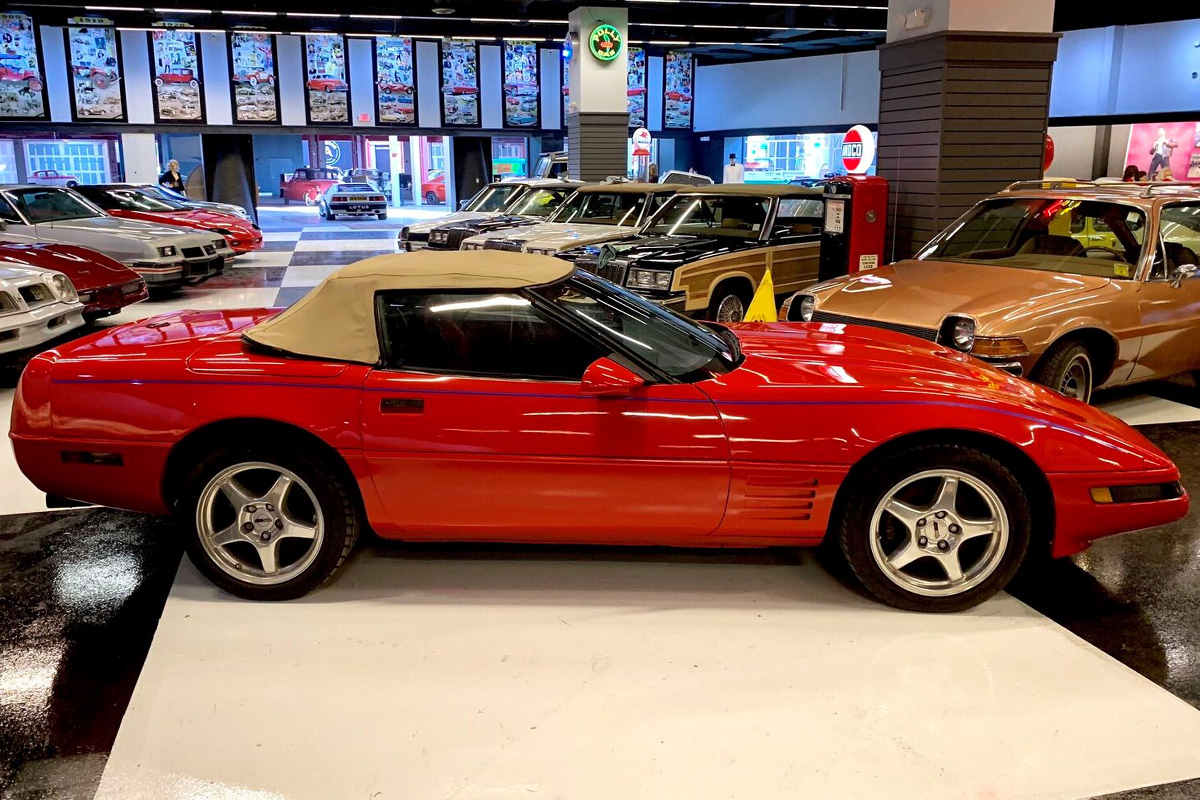

The 1988 Corvette included chassis design updates to fit the new 17 x 9.5 inch “Cuisinart” rims. The tires that housed the rims were P275/40ZR-17 Goodyear Eagle GT Tires, which got classified as “Z-rated.” This package was only available for the Z51 and Z52 suspension upgrades; however, the base model included 16 x 8.5-inch rims with P255/50ZR-16 Z-rated tires. The purpose of these new wheels was to sustain fast speeds. Chevy remodeled the suspension geometry to add a “zero scrub radius.”
Chevrolet also issued a white 35th Anniversary Edition Corvette this year. The company manufactured 2,000.
1989
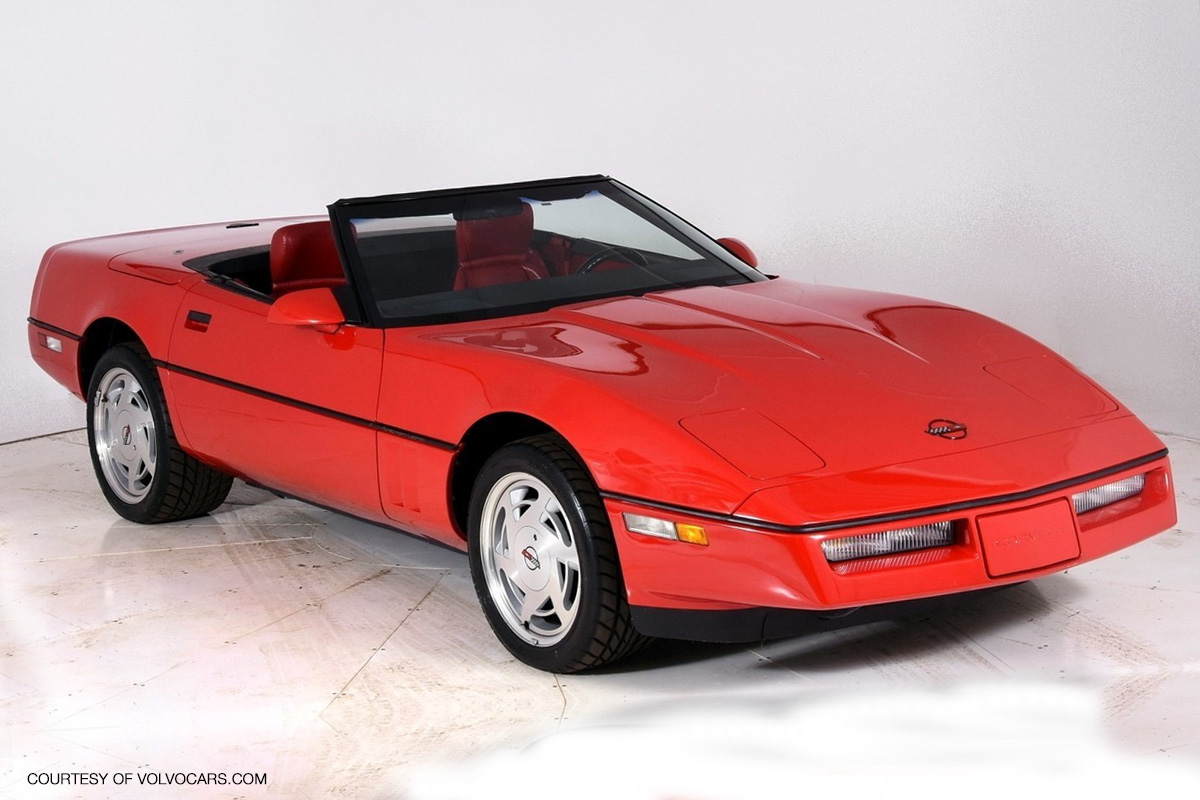

The Z52 option from previous years became standardized in all models of the 1989 Corvette. In addition to gaining Z52 equipment, seventeen-inch wheels and tires replaced the 16-inch setup from years prior. A new Z6 six-speed transmission was also included and accepted by consumers as a vast improvement over Dough Nash’s 4+3 manual transmission. The same year Chevrolet unveiled a new Z-R1 edition at the Geneva Auto Show. It had a 375 horsepower LT-5 Engine developed by Tony Rudd and his engineering team. The ZR-1 would not be available until the 1990 model year for the public, but Chevy built eighty-four for testing and exhibition. Despite not coming out that year, the dominant news cycle of the Z-R1 caused an increase in sales.
1990
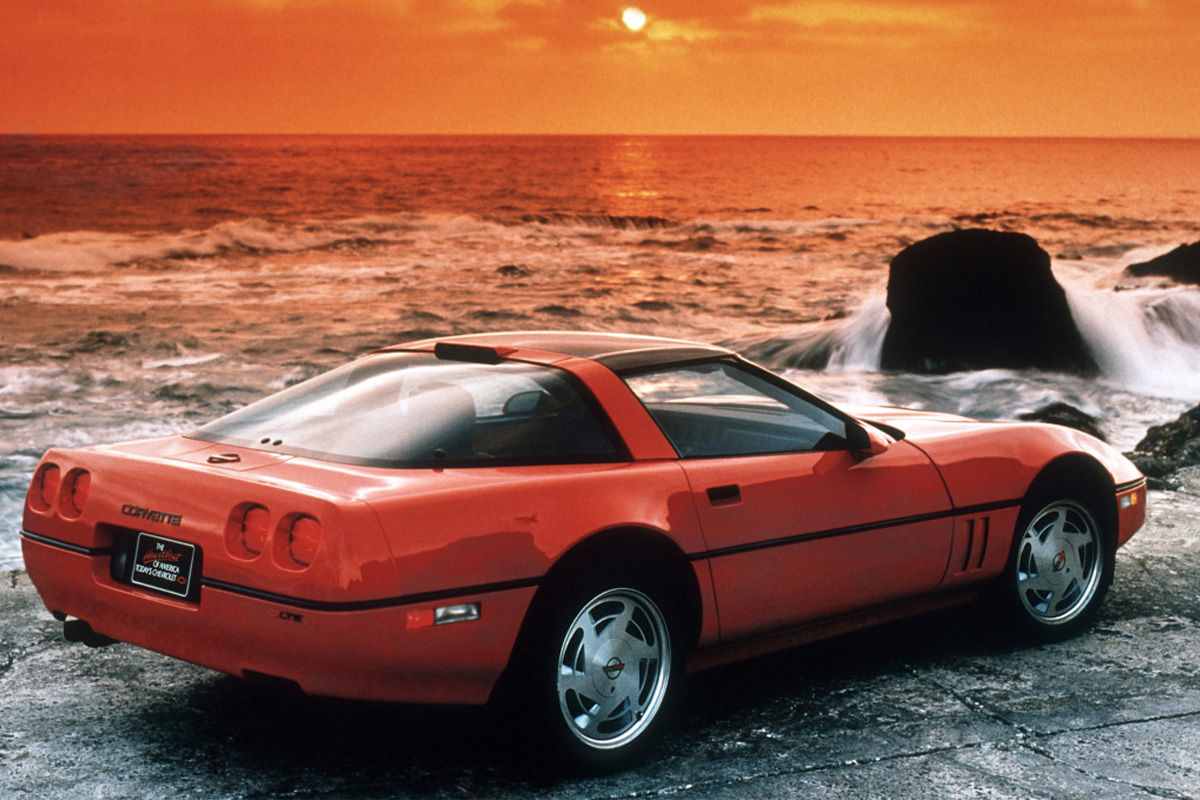

The 1990 Corvette was incredibly anticipated with the release of the ZR-1, which Chevy initially slated for the previous year. It had a 350 cu in the DOHC LT5 engine with a 375 hp rating. The rest of the editions saw improvements too, including the supplemental inflatable restraint (SIR) airbag system, which placed a standard driver’s side airbag in every vehicle. The Corvette also received an upgraded antilock-braking system, which allowed better handling plus an improved L98 engine. An optional feature available this year was the “Gold” 200 watts six-speaker sound system. Despite the hype, sales slightly dropped when comparing the 1989 model.
1991
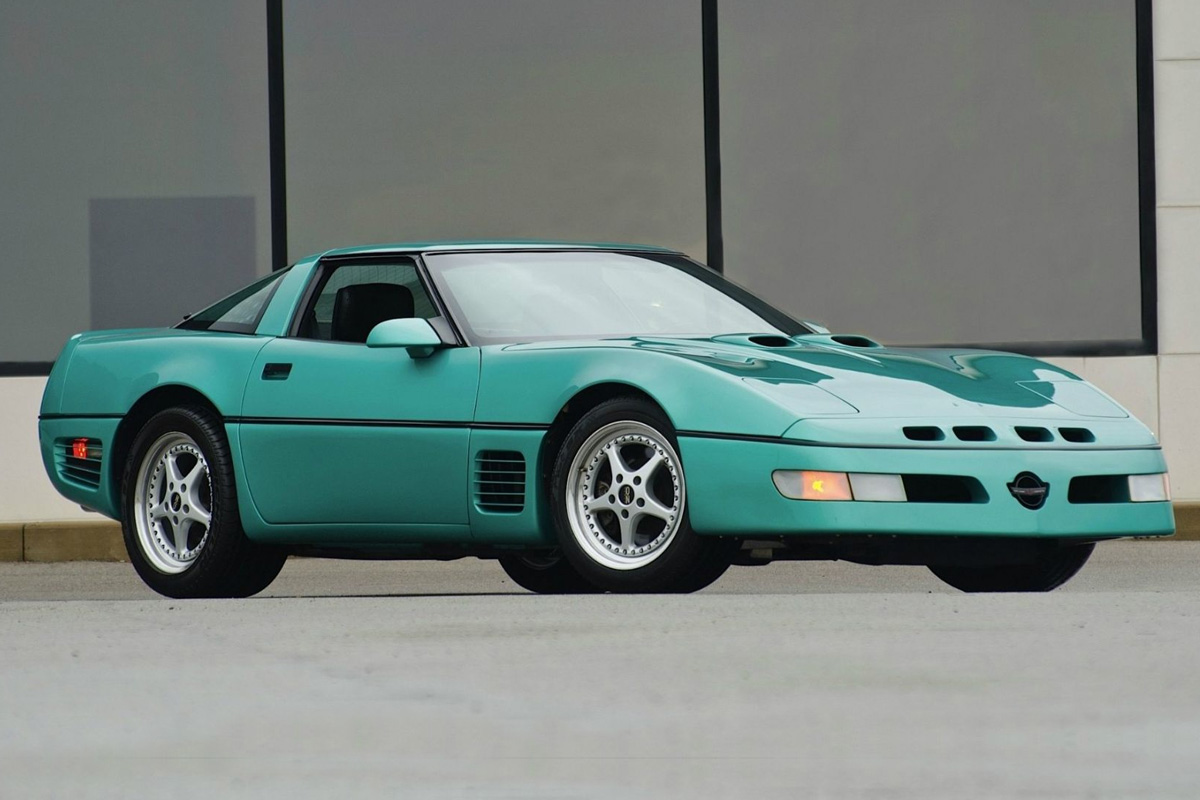

The changes for the 1991 Corvette were mainly cosmetic. The exterior received horizontal front-fender strakes, a slimmer front fascia along with a wider body-side molding. The wheels even saw a slight change. The base models also began resembling the ZR-1 edition, which may have hurt the ZR-1 in sales, given the significant price differences. A quick notable fact, 1991 was the last year Chevrolet offered the Callaway B2K twin Turbo.
Mechanically, the 1991 Corvette had a new-power delay feature for the audio system, a new “low oil” indicator. The exhaust system also saw some updates.
1992
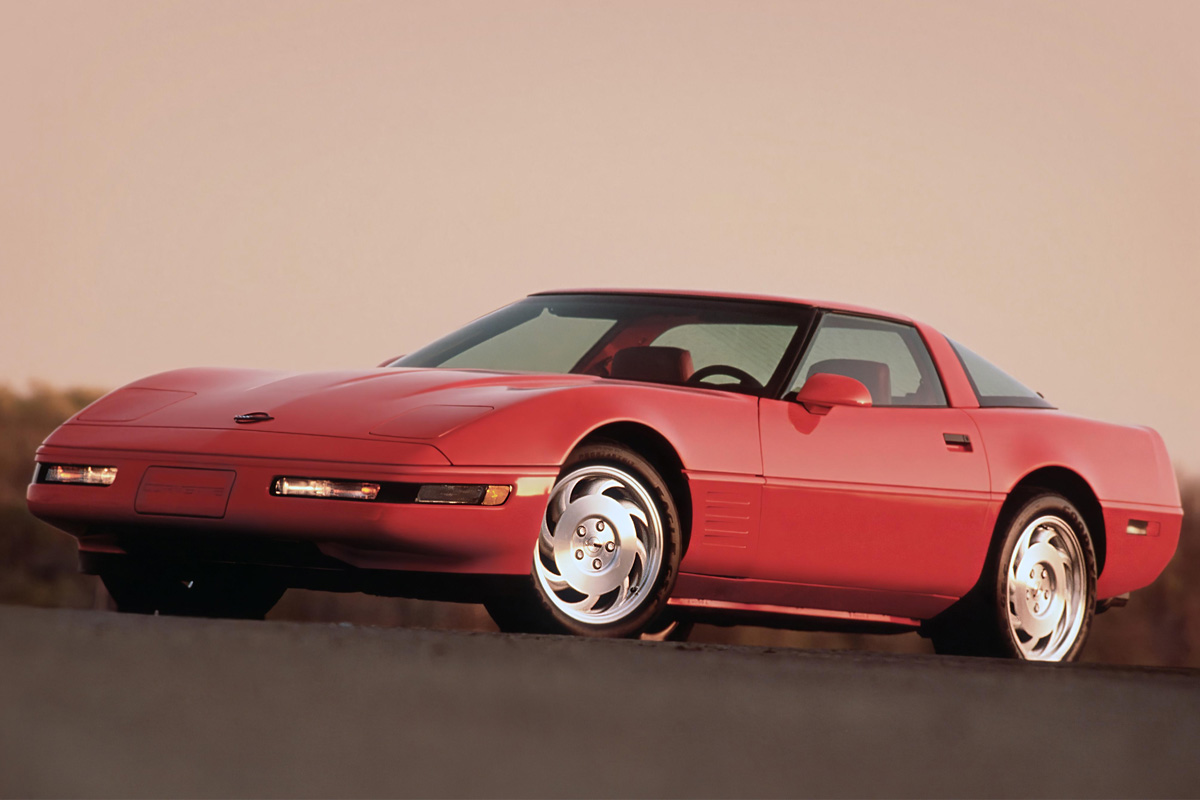

For the 1992 Corvette, a traction control system titled Acceleration Slip Regulation (ASR) became standard. The system used ABS sensors to operate the brakes to keep traction when it identified rear-wheel slip. In certain circumstances, the driver would feel the brake pedal push back on their foot to signal that the system was working. The ASR could be switched off on the dashboard. The other big addition for 1992 was the new LT-1 Engine, which replaced the L98. The Engine was 5.7 L 350 cu in and used a reverse-flow cooling system.
1993
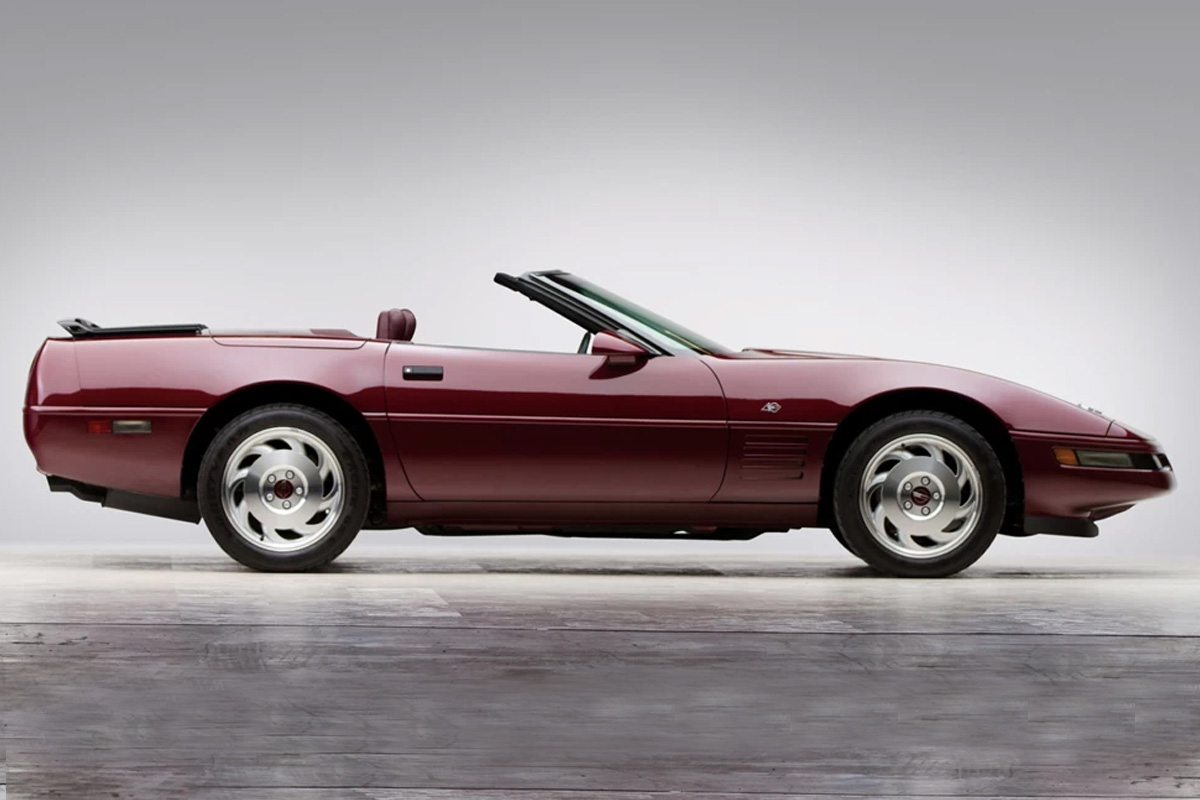

The 1993 Corvette went mostly unchanged from the previous model minus some minor mechanical and cosmetic tweaks, such as cutting down the LT-1 Engine noise. The biggest innovation Chevrolet included was a passive keyless entry (PKE) system. Essentially if the driver were close to their car with their keys, it would atomically unlock. If you were looking for something faster, on the other hand, Chevy offered a 40th Anniversary Edition Corvette. The car used a 9.4 L (572 cu in) Chevy V-8 and a GM four-speed automatic transmission. When the vehicle is fully open, it could go up and hold 218 per hour.
1994
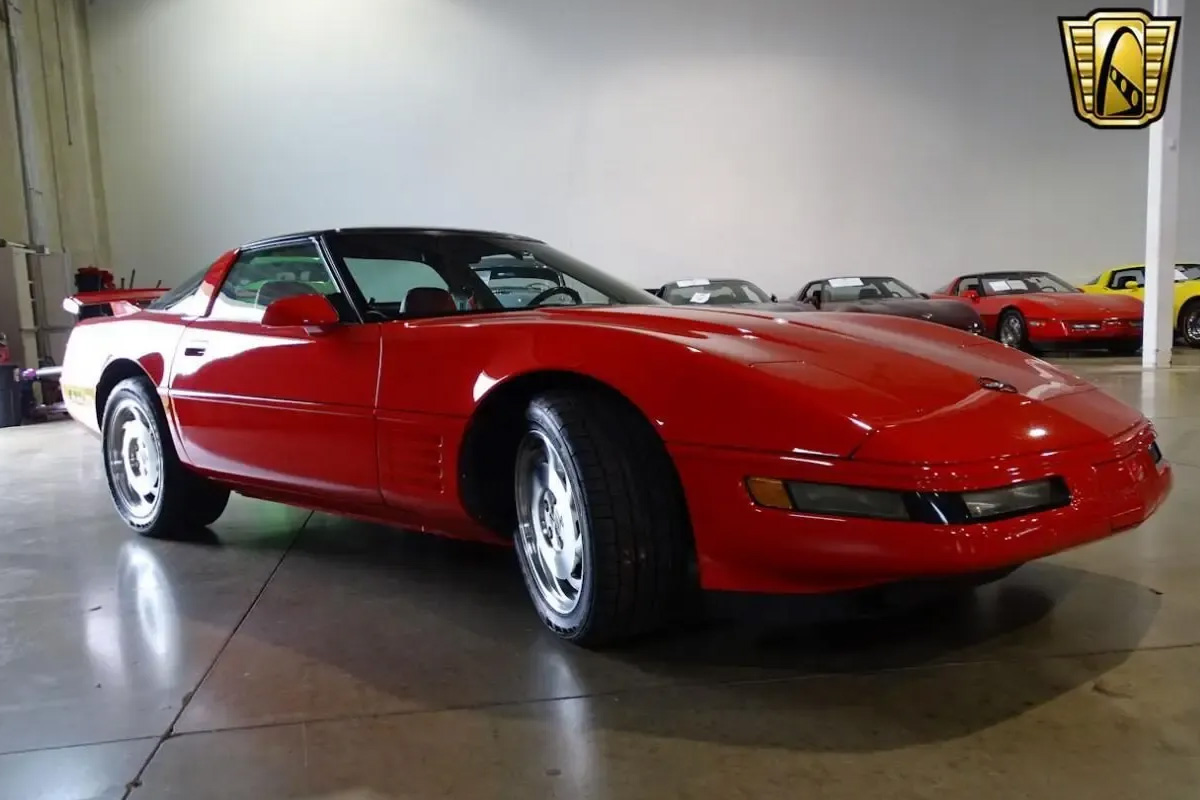

1994 was another model year without any significant changes. The 1994 Corvette saw a more powerful ignition system for its LT- Engine, which resulted in quicker starting times even in cold temperatures. A new sequential fuel injection system was also included to improve drivability, throttle response, and drop tailpipe emissions. Chevrolet added a passenger-side airbag plus a knee bolster to comply with safety requirements “passive restraint” from the federal government.
1995
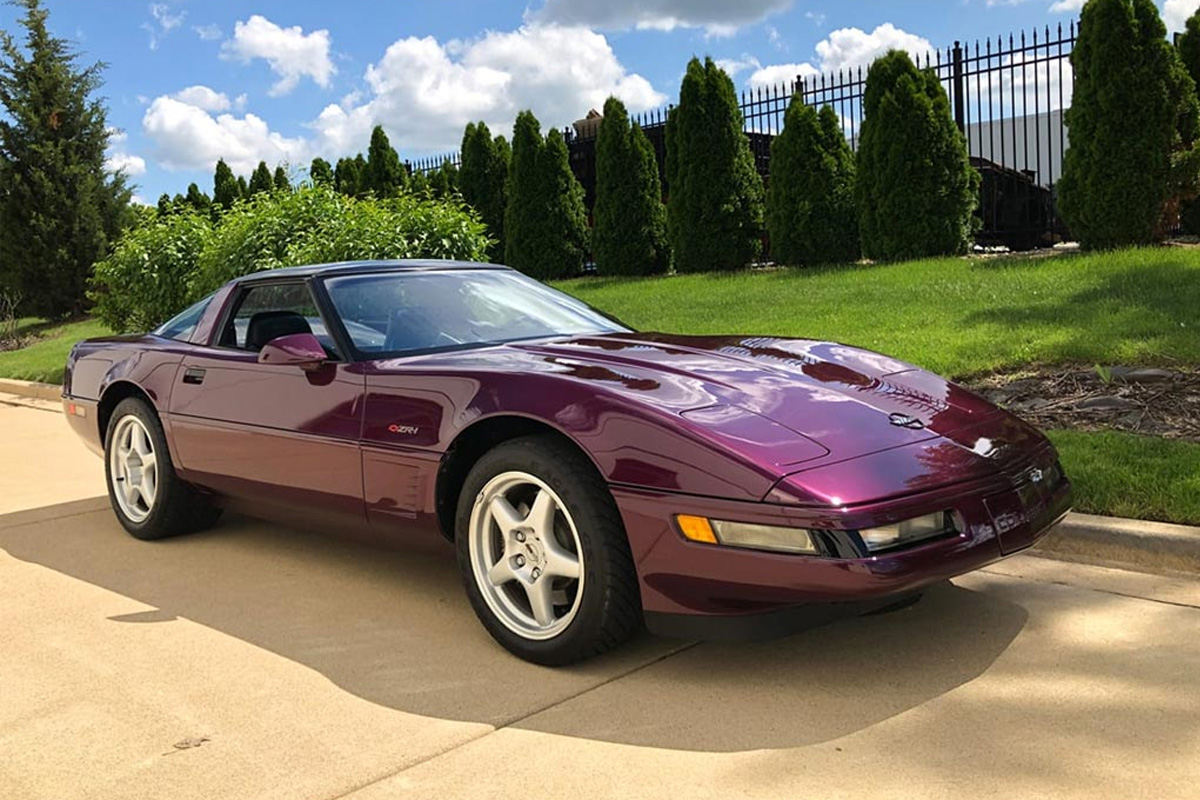

Once again, the 1995 Corvette only saw minor changes mechanically and cosmetically. The LT1 Engine saw some improvements, including tweaked connecting rods for better strength and weight uniformity, a quieter engine fan, and the fuel injection system could take alcohol blend fuels. Also, the updated fuel injectors helped reduce fuel drippage when the car was not in use. Another revision was the six-speed manual transmission now worked with the high-detent operation, and heavy-duty ZR-1 brakes became standard. As for the exterior, the 1995 Corvette had redesigned fenders. It is the easiest way to identify the new model. 1995 marked the last year of the ZR-1, which ended early in the production cycle. We should note the Opti-Spark Ignition System has trouble with this C4.
1996
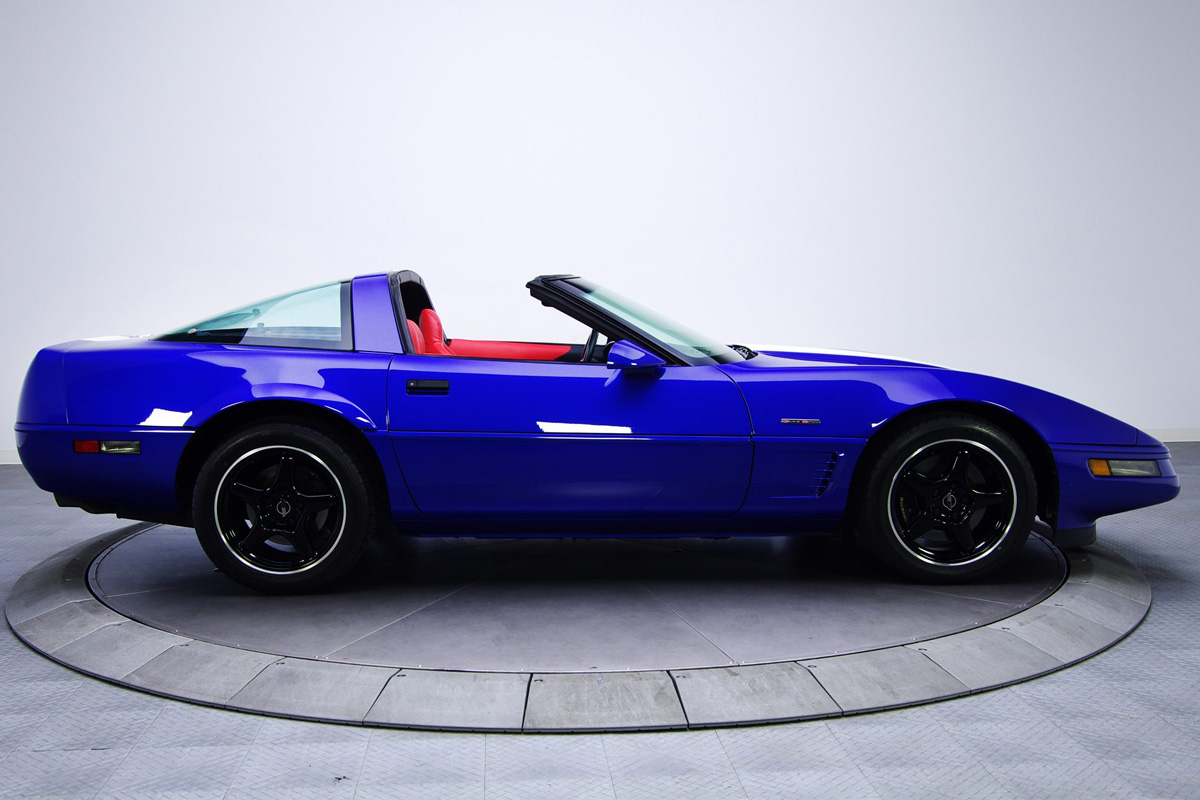

The 1996 Corvette was the last of the C4 models Chevrolet released. As a result, the company wanted to give special editions to honor the generation: The Collector Edition and the Grand Sport special edition. These vehicles included a revived LT1 Power plant and the LT4 ( a high-performance variant of the LT1 with 330 hp). The 1996 Corvette was the only C4 to include an OBD II diagnostics and have Real-Time Damping as an option. This year, Chevy saw a slight increase in sales.
1997
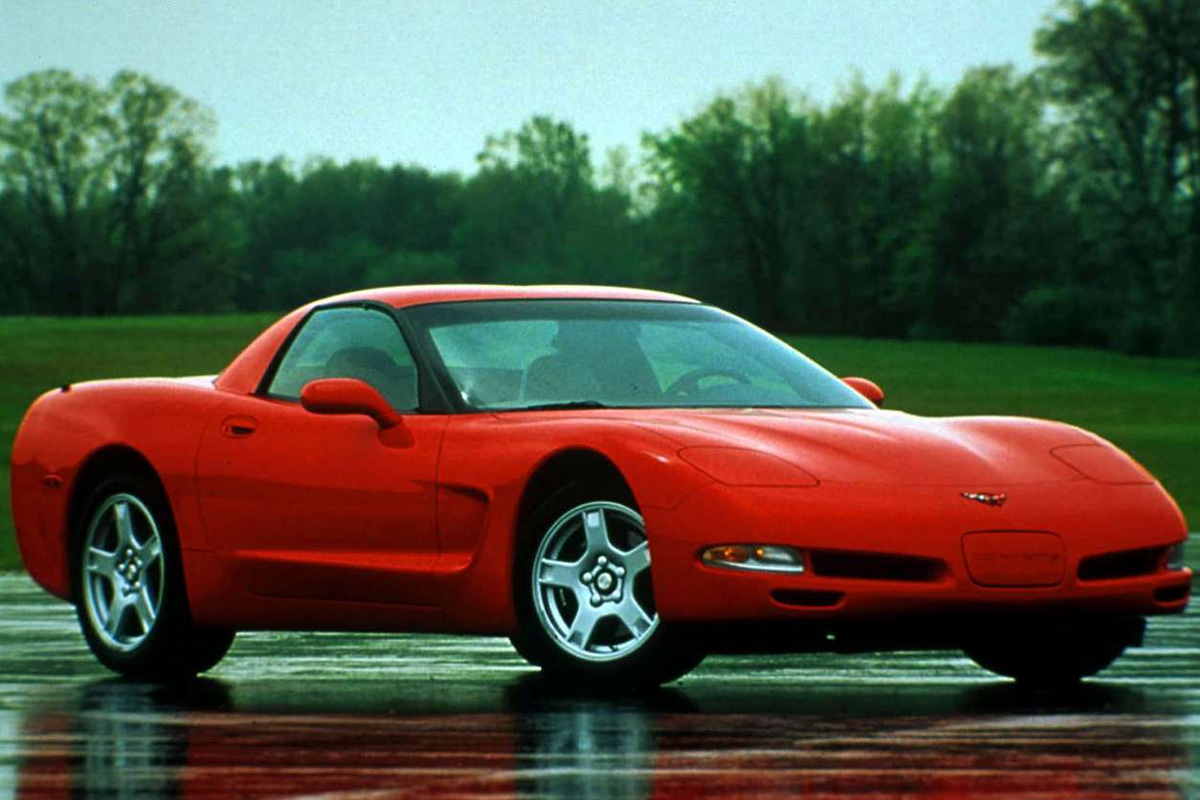

At long last, the C5 Corvette released. Chevrolet began toying with Corvette’s next generation as early as 1992, but they didn’t start building them until 1996. The vehicle was completely redesigned with a sleek new look ready for the approaching millennium. It had many new concepts, and building breakthroughs, including a hydroformed box frame and a new LS1 aluminum engine, rated a 345 bhp. According to designer Jon Albert, the goals they accomplished with the C5 model were “improved performance, reduced mass, and increased reliably with the whole car’s overall framework.” The C5 received a reputation as one of the fastest Corvettes of all time, and in 1997 was considered the fastest commercial car in the world that year. For 1997, Chevy only offered a fastback coupé.
1998
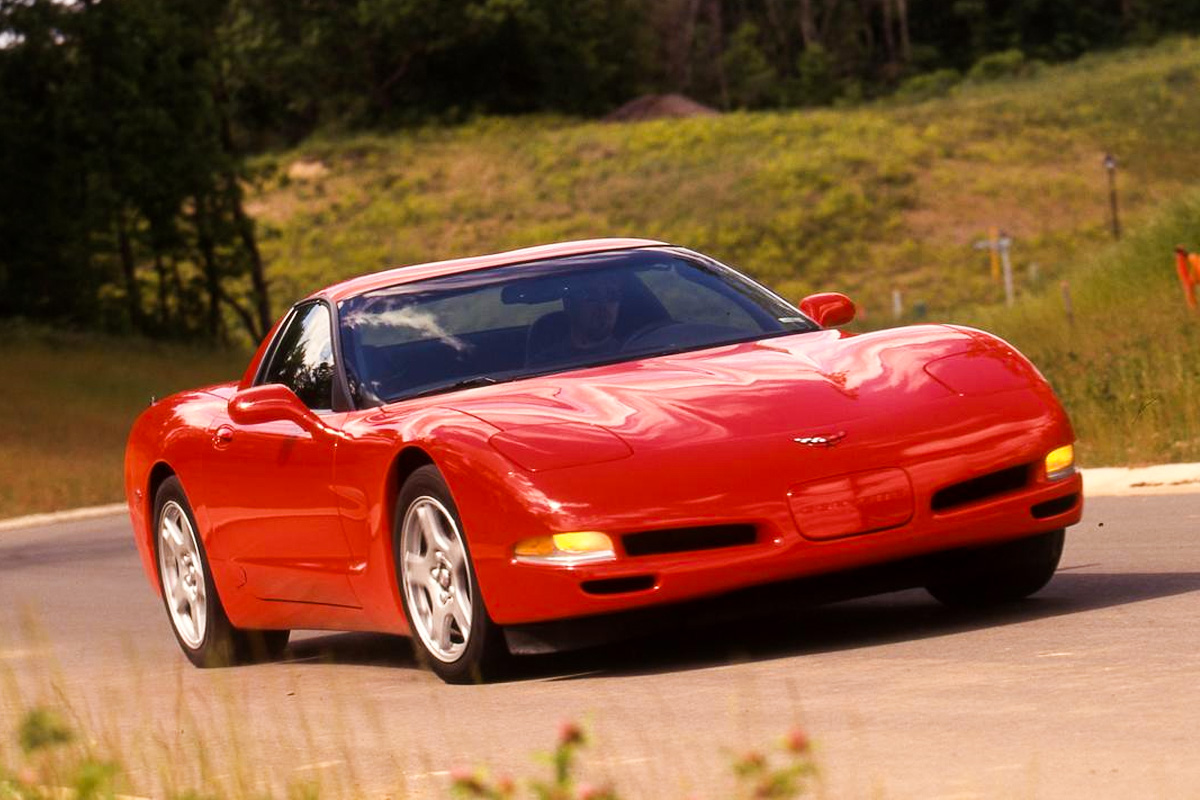

C5 Corvette was a major success with critics applauding the design, performance, and drivability. For the 1998 Corvette, Chevrolet decided to reintroduce the convertible edition. This convertible would have a functioning trunk, which is the first time Chevy included one since 1962. The 1998 model also came with an optional $500 Active Handling System. The system works because it activates when it detects the distinction between how the driver intends for the car to corner and how it actually corners. The system then applies four brakes to correct the issue. Lastly, dealerships sold Indianapolis 500 Pace Car Replicas this year.
1999
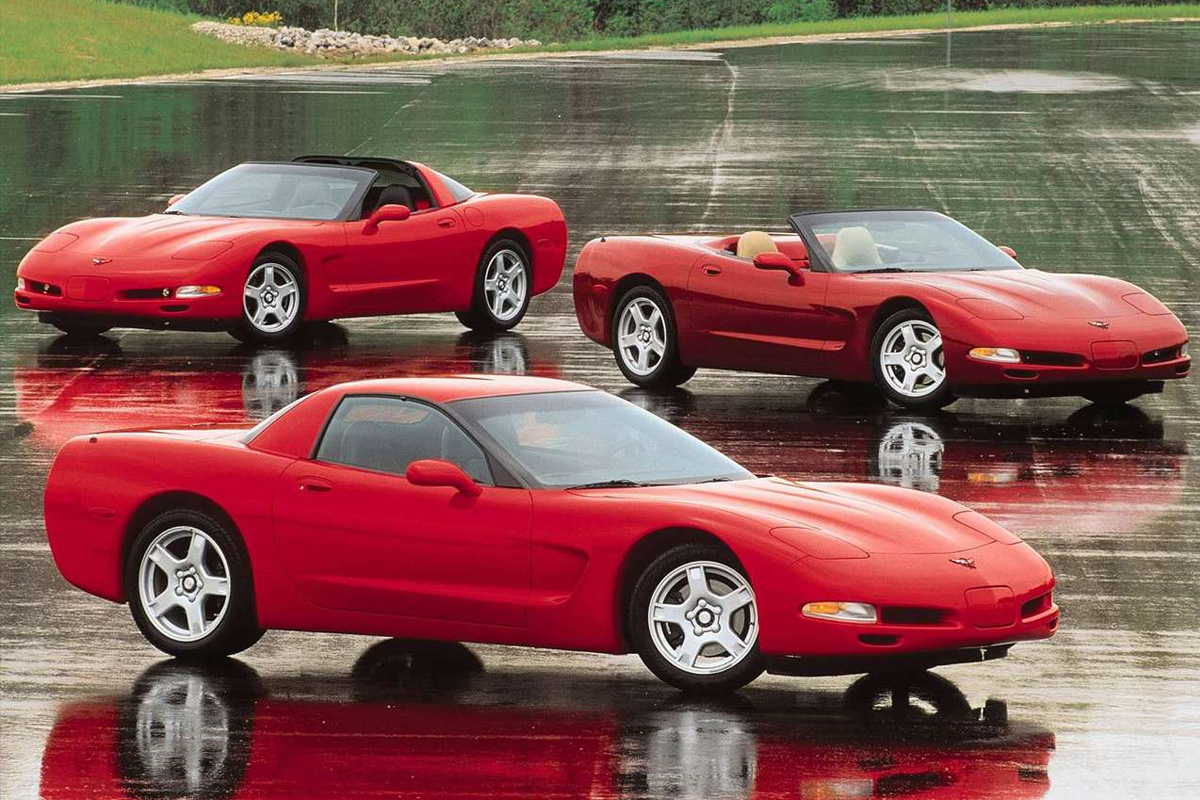

From the start of Chevrolet’s development of the C5, they looked at making a budget variant of their vehicle. They stripped amenities, gave it manual windows, and cloth seats. Initial surveys for their proposed car received adverse reactions from participants at a research center, causing the company to go back to the drawing boards. For the 1999 Corvette, their less expensive version released. Instead of focusing on luxury, Chevrolet stripped features and centered the design on performance. Chevy titled the vehicle the FRC Corvette (Fixed Roof Coupe). It weighed 92 pounds less than the standard coupe and came with a set hardtop. The car was basically a convertible with a fixed fiberglass roof. Surprisingly it only cost $394 less than the standard coupe and was only slightly faster. Besides the FRC, the 1999 Corvette came with a magnetically variable power-steering system that helped the car from “wandering” at higher speeds. Chevy also offered a “Heads-Up-Display” and “Telescoping Steering Column.”
2000
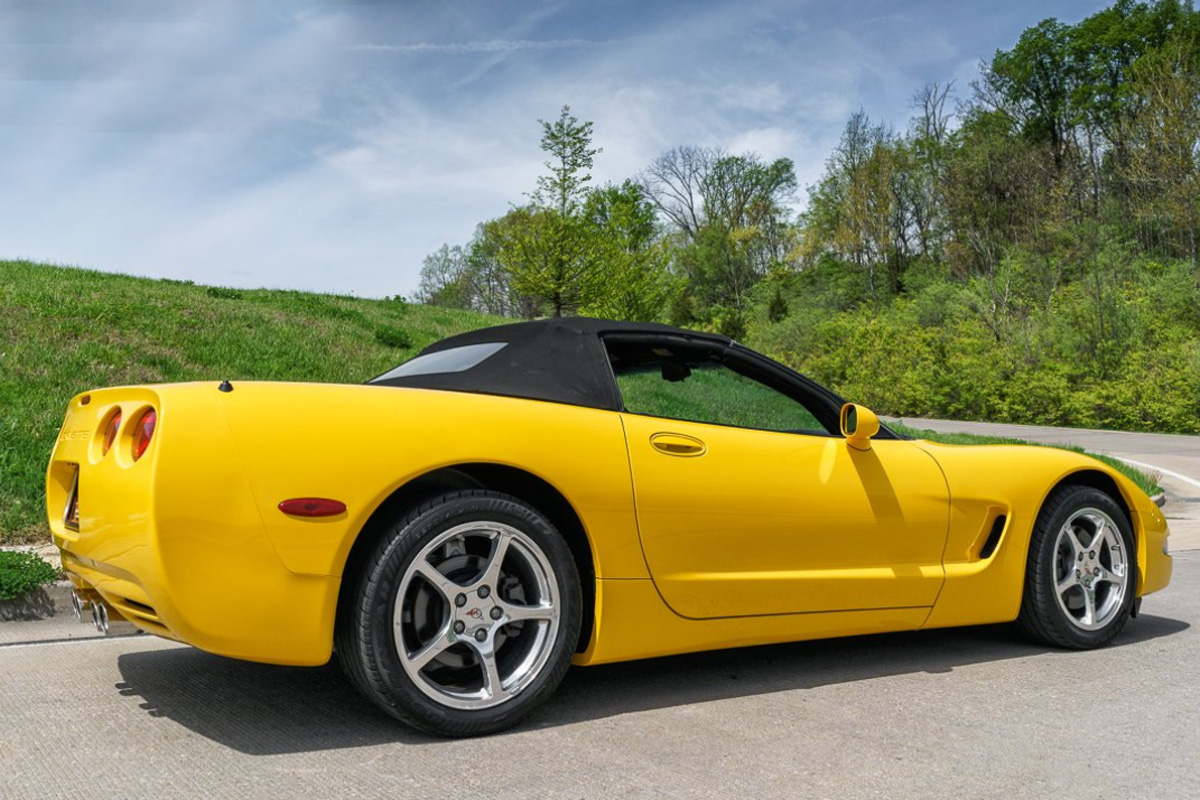

With the millennium now here, Chevrolet issued the 2000 Corvette. It did not see many changes cosmetically or mechanically. However, they did unveil new colors, including Magnetic Red II, Dark Bowling Green, and millennium yellow. The Z51 Performance Handling Package also received larger stabilizer bars on both the front and rear. Most improvements to the base model focused on ride stability and drivability with engineers enhancing the Selective Real-Time Damping suspension. Another big difference with this model is it included newly styled alloy wheels, which had flow-formed rims for improved durability.
2001
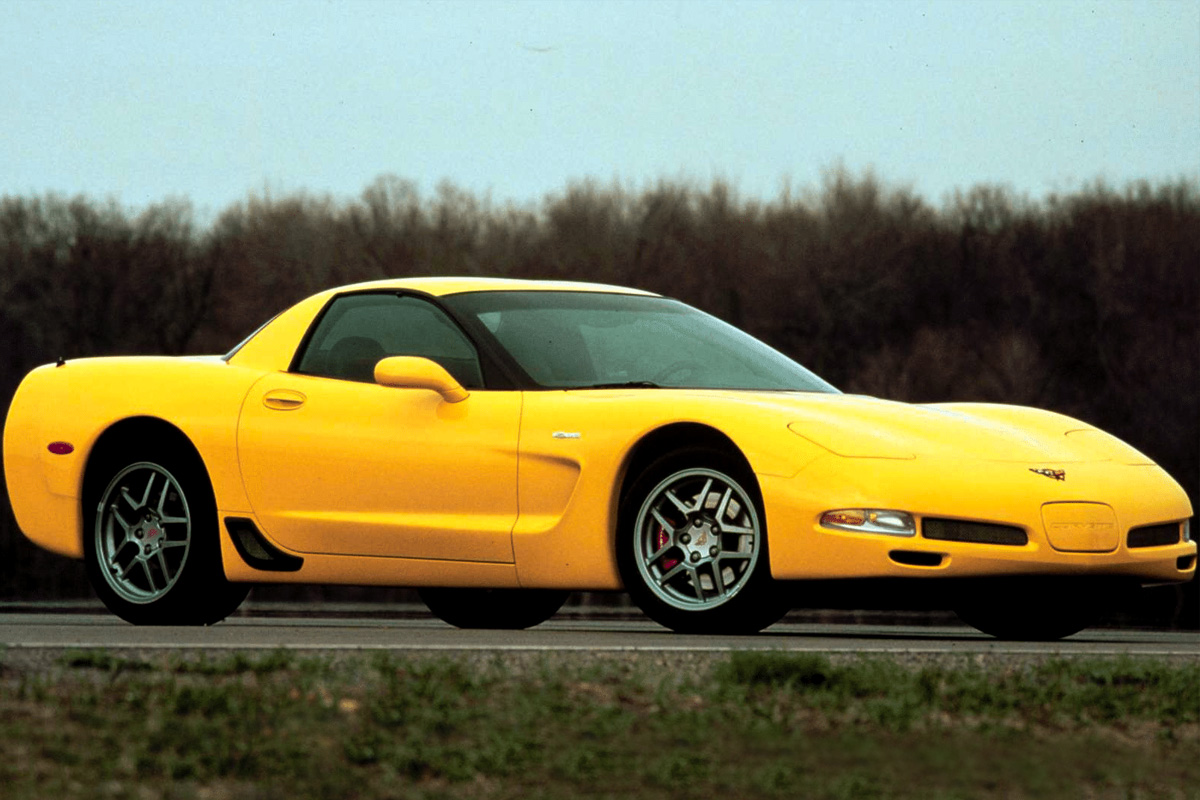

David Hill, Corvette’s Chief Engineer, was not satisfied with the current C5 performance and wanted a vehicle that was genuinely “race-ready” out of the gate. He believed some drivers cared more about speed than comfort. Built off of the Fixed Roof Coupe (FRC), this replacement would compete with horsepower and performance numbers of the C4 ZR-1 and be significantly cheaper. The result was the Z06 Corvette, named after the original Z06 package from the 1963 Corvette. Its LS6 Engine (named after the 1971 LS6 designation) boasted 385 horsepower and 385 lb-ft of torque. The vehicle also had suspension enhancements over its predecessor models. The rest of the 2001 Corvettes all came with a Second-Generation Active Handling System and received a minor boost in engine power.
2002
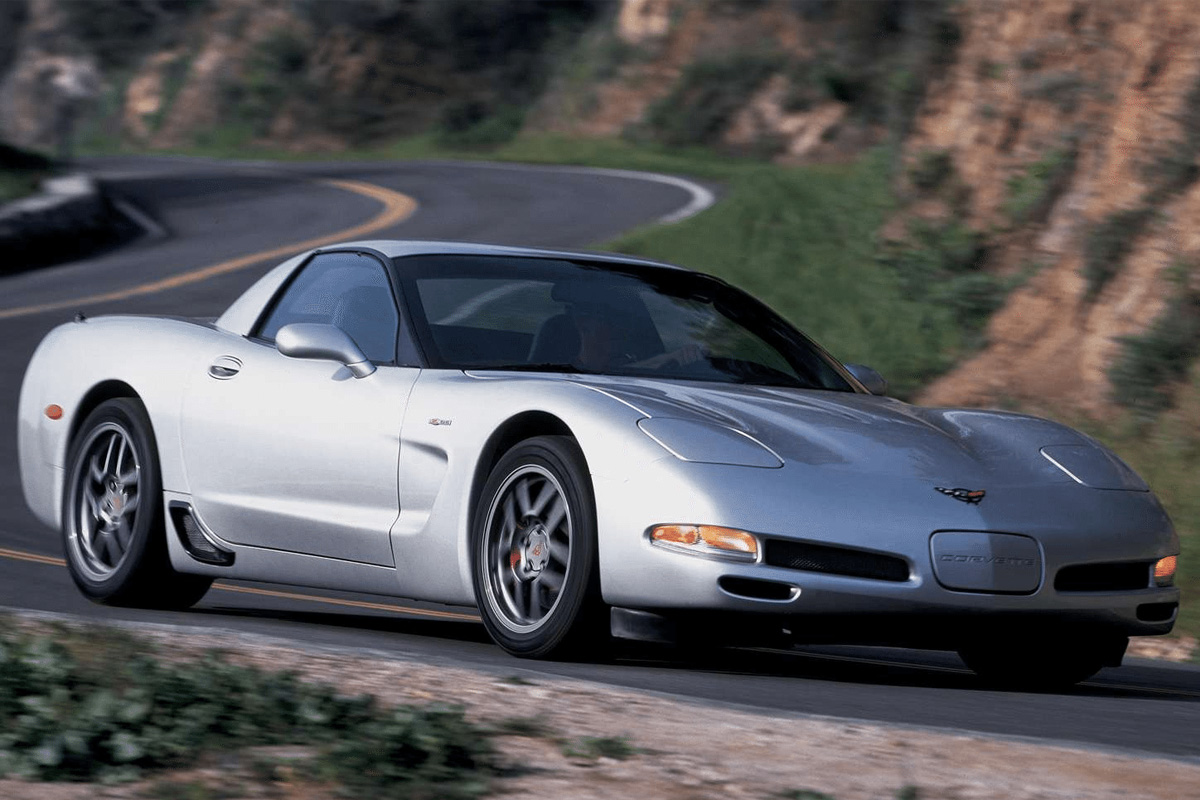

Chevrolet put the spotlight on the 2002 Z06 Corvette. The vehicle’s 5.7-liter LS6 Engine obtained a 20 hp increase bringing the Z06 to a 405 brake-horsepower. It also received an additional 15 lb-ft of torque. This feat was possible due to a new cam profile that permitted the intake and exhaust of the Engine’s valves to widen an extra .7mm, which made Engine to breathe more freely. As for the other models, they received an in-dash AM/FM/CD player. For those vehicles with an automatic transmission, Chevrolet put in a lighter-weight transmission cooler.
2003
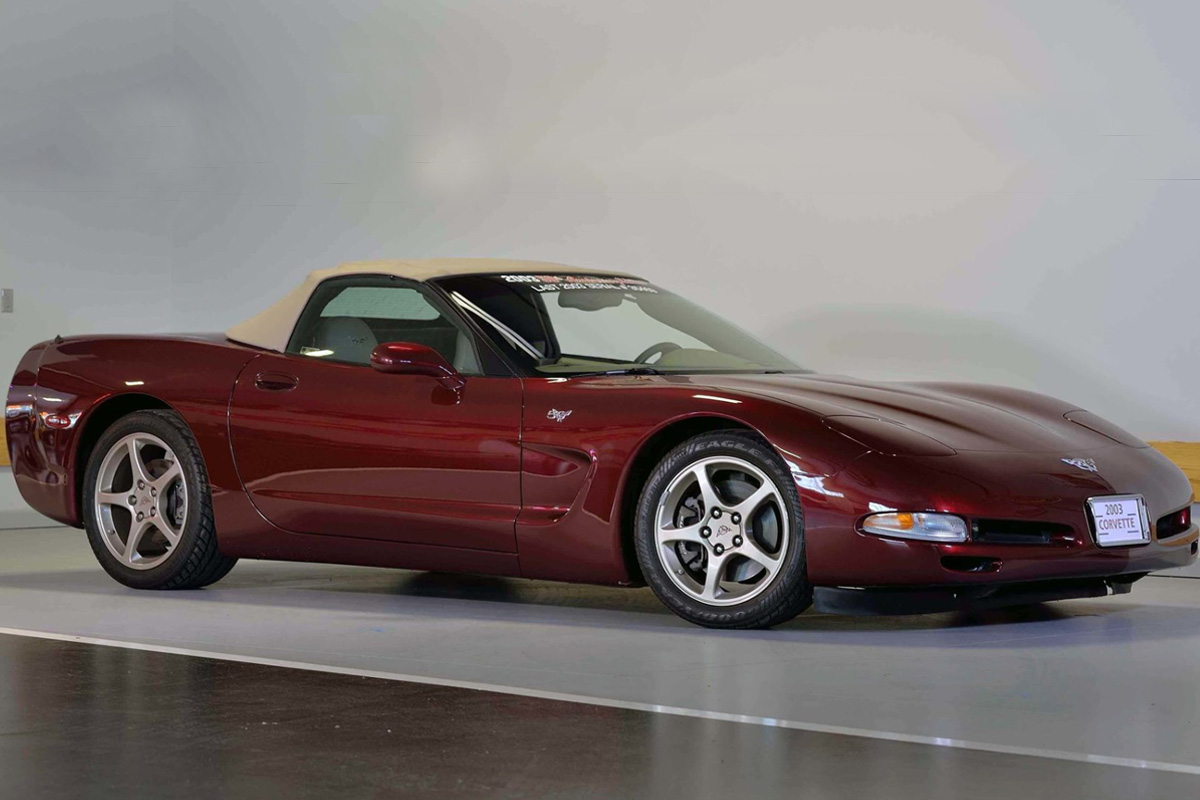

In honor of 50 years of the Corvette manufacturing, Chevrolet issued a 50th Anniversary Edition package for the convertible and coupe. It had a special metallic-burgundy Anniversary Red exterior with “anniversary edition” decals. It also came with champagne colored wheels. The interior also saw unique detailing. Additionally, the 2003 Corvette received an F55 Magnetic Selective Ride Control suspension designed to make more than 1,000-minute adjustments per second. How it worked was the system had a computer chip with the suspension that controlled the car’s ride using the vehicle’s speed, steering-wheel angle, braking, and outside temperature. The purpose of the system was to give the driver a smoother ride minimizing noise and bouncing. Most critics admitted it helped with drivability, though noted the extra weight (13 pounds). The F55 option was not included in the Z06.
2004
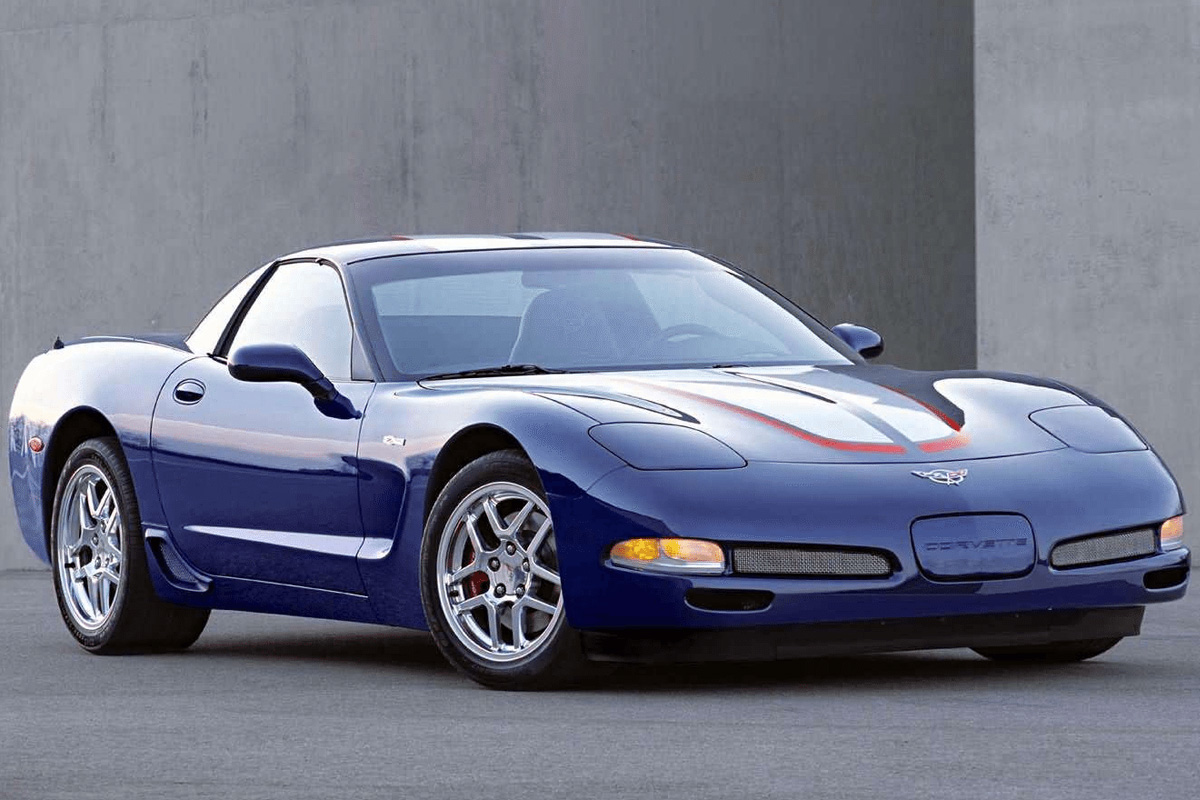

2004 marked the last year of the C5. Chevrolet decided against putting any radical changes in this year’s Corvette. What they did offer was a 24 Hours of Le Mans Commemorative Edition package. You can see one in the picture above. The Commemorative Z06 model costs $4,335 more than the standard coupe. It had a carbon-fiber hood that decreased the nose weight by 10.6 pounds. The C5 definitely was a generation to remember.
2005
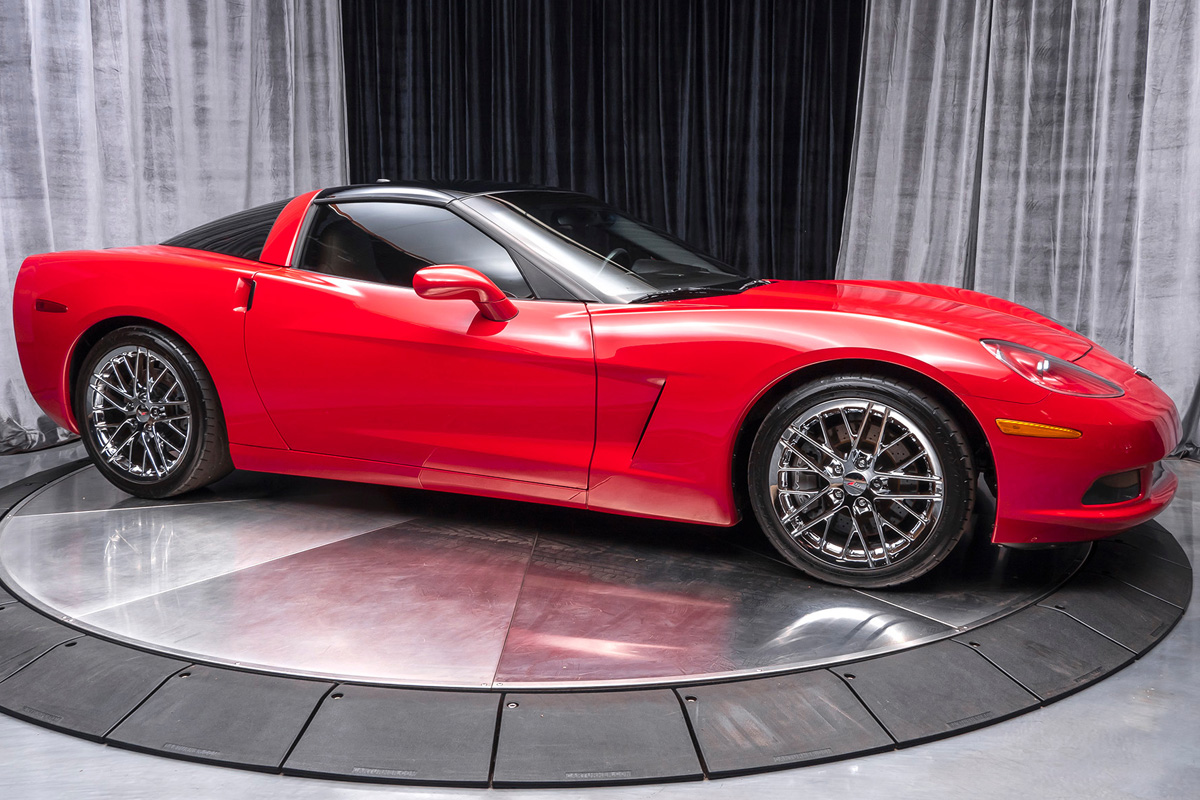

The Corvette C6 hit the market in 2005. It was not a total redesign like its predecessor. However, the vehicle did receive some sweeping changes, including new bodywork—other alterations comprised of exposed headlamps, larger passenger compartment, and modified suspension with longer-stroke shock absorbers. The most significant change was probably underneath the hood. The 2005 Corvette had a 6.0 liter 364 cu in V-8 (LS2) with a 400 horsepower rating. Surprisingly the base coupe was less than the 2004 Corvette while the convertible model was more expensive. The 2005 Corvette was incredibly well received by critics making Car and Drivers annual “10 Best” list. Sales increased this year, but probably not at the rate Chevrolet hoped.
2006
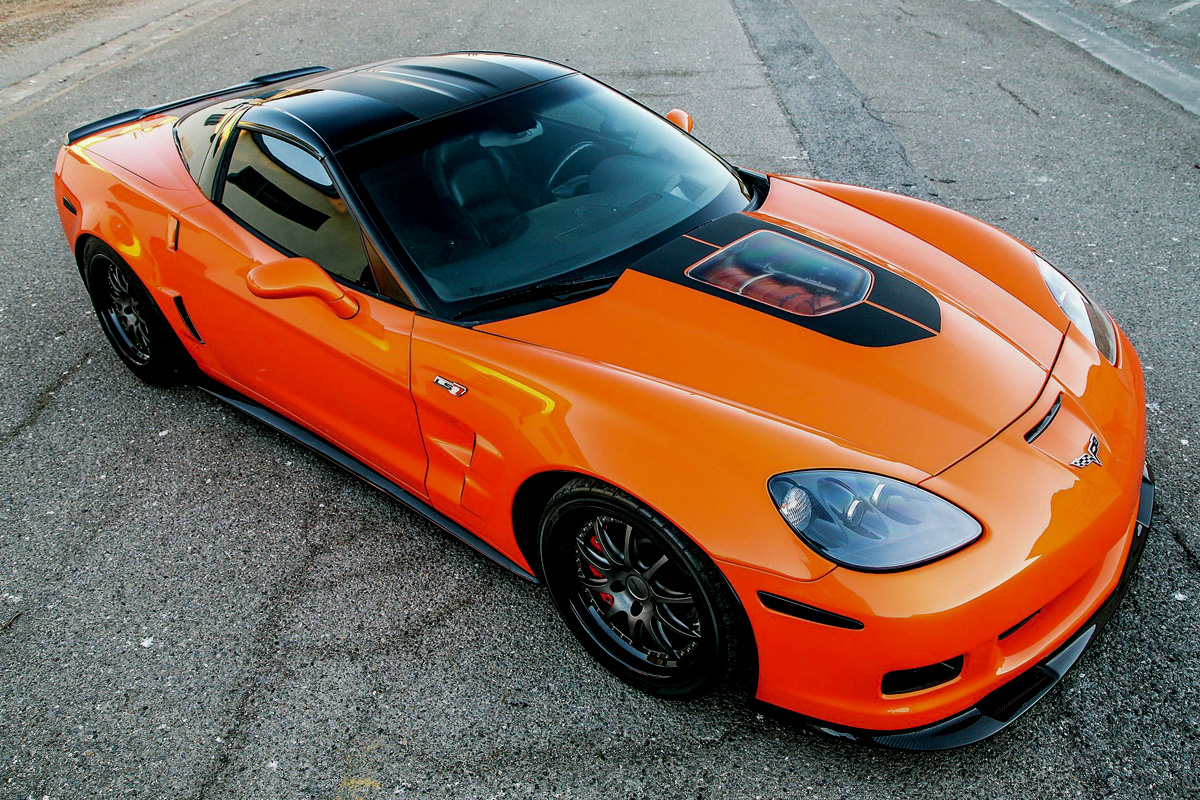

The 2006 Corvette saw little change from the previous year. The most substantial addition to the lineup this year was the return of the Z06. The Z06 was designed for high-speed aerodynamic performance. Like the C5 Z06 models, the C6 included a fixed roof. This year’s Z06 also had the C6 Uni-frame structure re-made with aluminum helping counterbalance the weight since it did have a notchback. For non Z06 models, a six-speed automatic transmission replaced the four-speed automatic transmission and included paddle shifters. It permitted the driver to switch between sport and manual control. Also new for the 2006 Corvette was a differential redesign.
2007
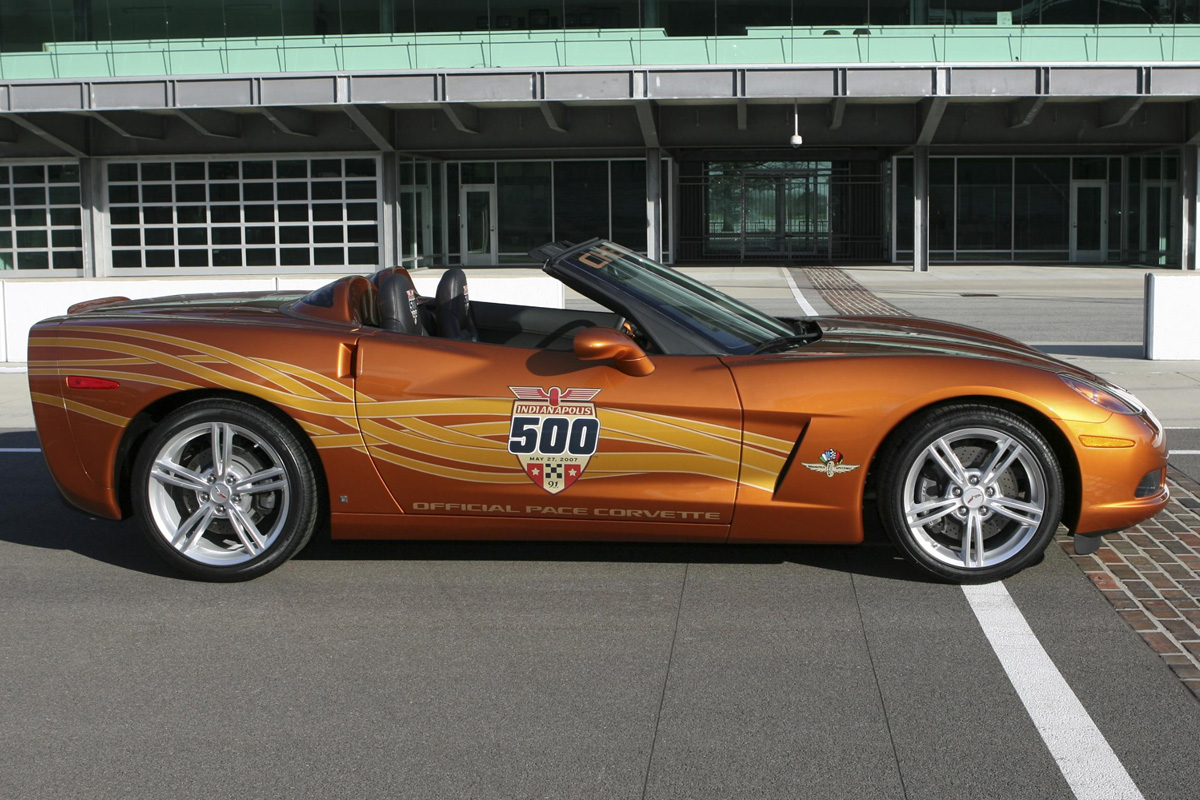

2007 Corvette barley saw any alterations. The most noticeable changes came in the interior. The ignition button had the word “ENGINE” labeled on it, steering wheels had controls for the steering wheels, and they came with larger gloveboxes. Also, Chevrolet sold new chair options for customers. As for the mechanics, cross-drilled brake rotors were available to customers who bought the Magnetic Selective Ride Control option (RPO F55). The real exciting thing for 2007 was the paint jobs and special editions such as the Ron Fellows Corvette. The one in the picture is a 2007 Indianapolis Pace Car Replica.
2008
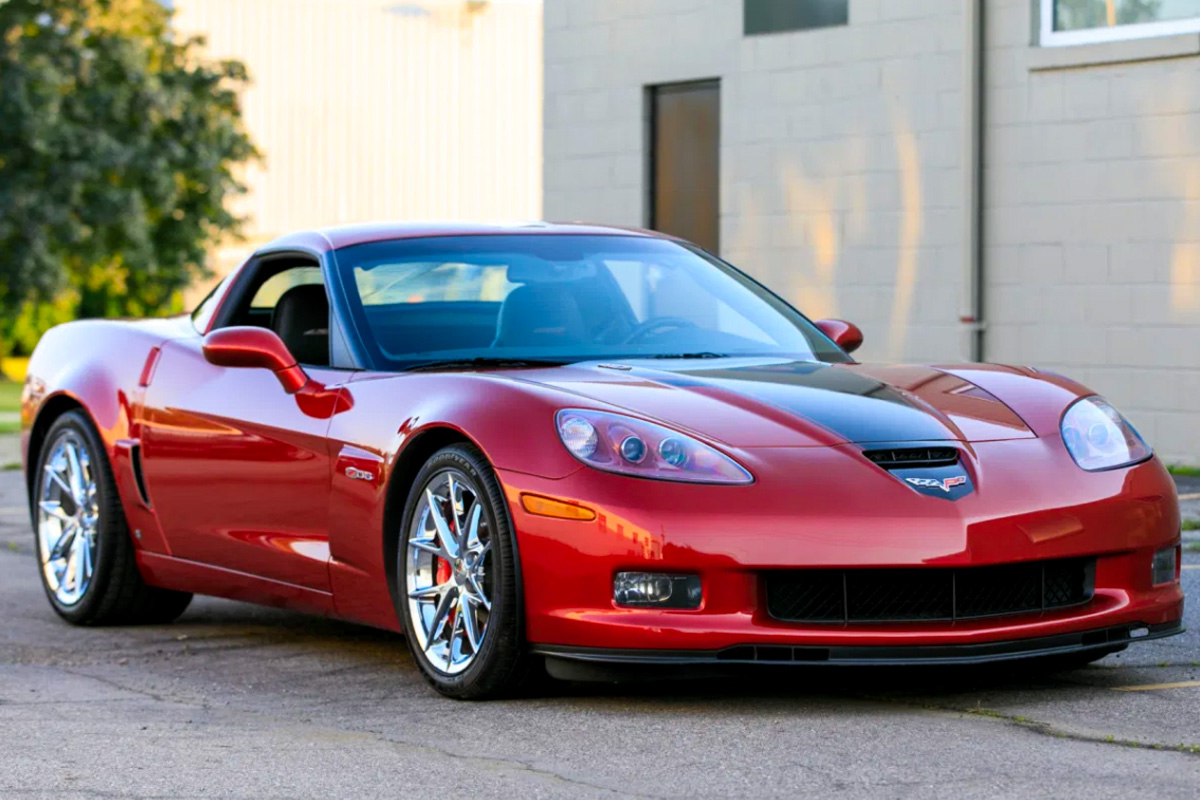

It is clear that Chevrolet was planning something big in 2008 since the previous year’s model saw little changes. The company revealed a new block engine, the LS3, which was 364 cu in. It came standard in the base coupe and convertible producing 430 horsepower (30 more than the LS2). Along with the engine change, these Vettes got a Tremec Tr6060 transmission and a new steering system with a firmer intermediate shaft and modified controller calibrations making for a better driving experience. The interior also saw an update with a “cyber” graphic pattern console trim plate and more. If you purchased the 4LT and 3LZ options, they now came with a leather interior.
2009
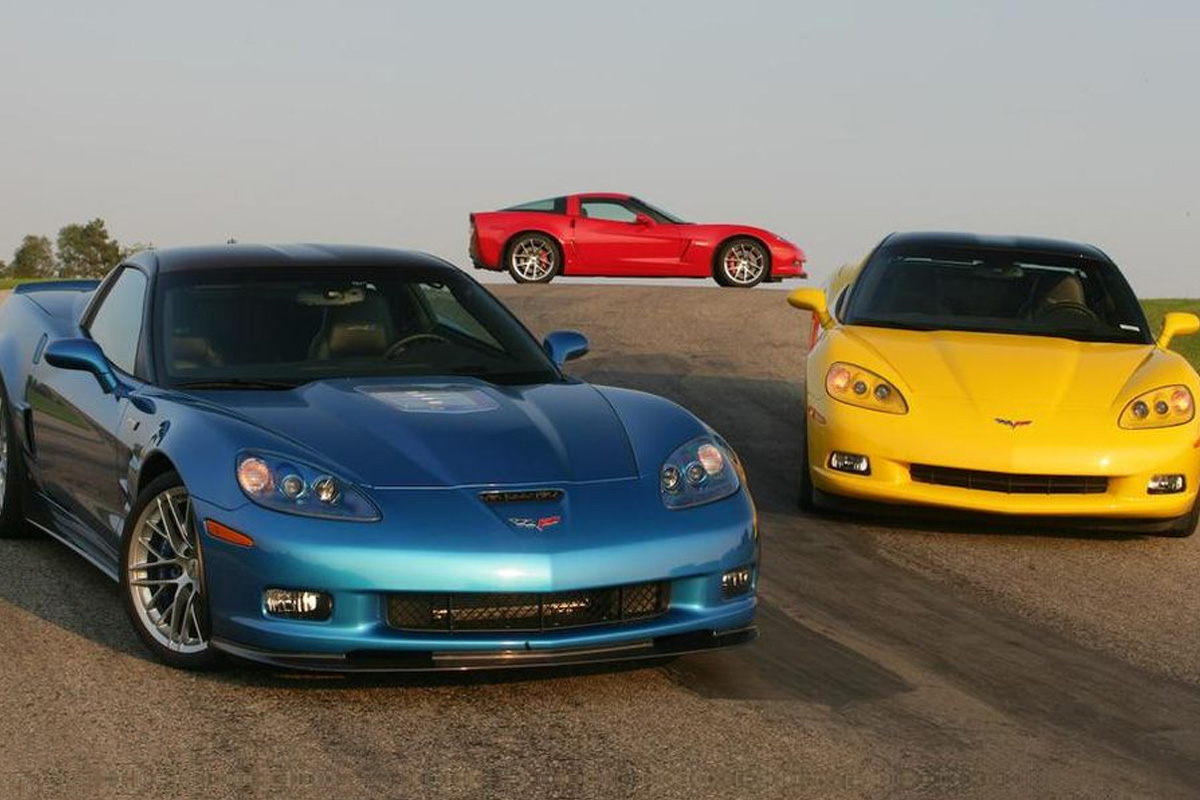
After years of rumors, the ZR1 made a return after a fourteen-year hiatus more powerful than ever. It was unrelieved in 2008 and announced for the 2009 Corvette lineup. The vehicle had a new LS9 supercharged 6.2 Litre V-r engine with a rating of 638 horsepower and 604 lb. /ft. of torque. One of the most distinguishable characteristics of the ZR1 was its raised, all-carbon-fiber hood and polycarbonate window. The Z06 saw new “Spyder” wheels, and the base models/convertible received Bluetooth functionality.
2010
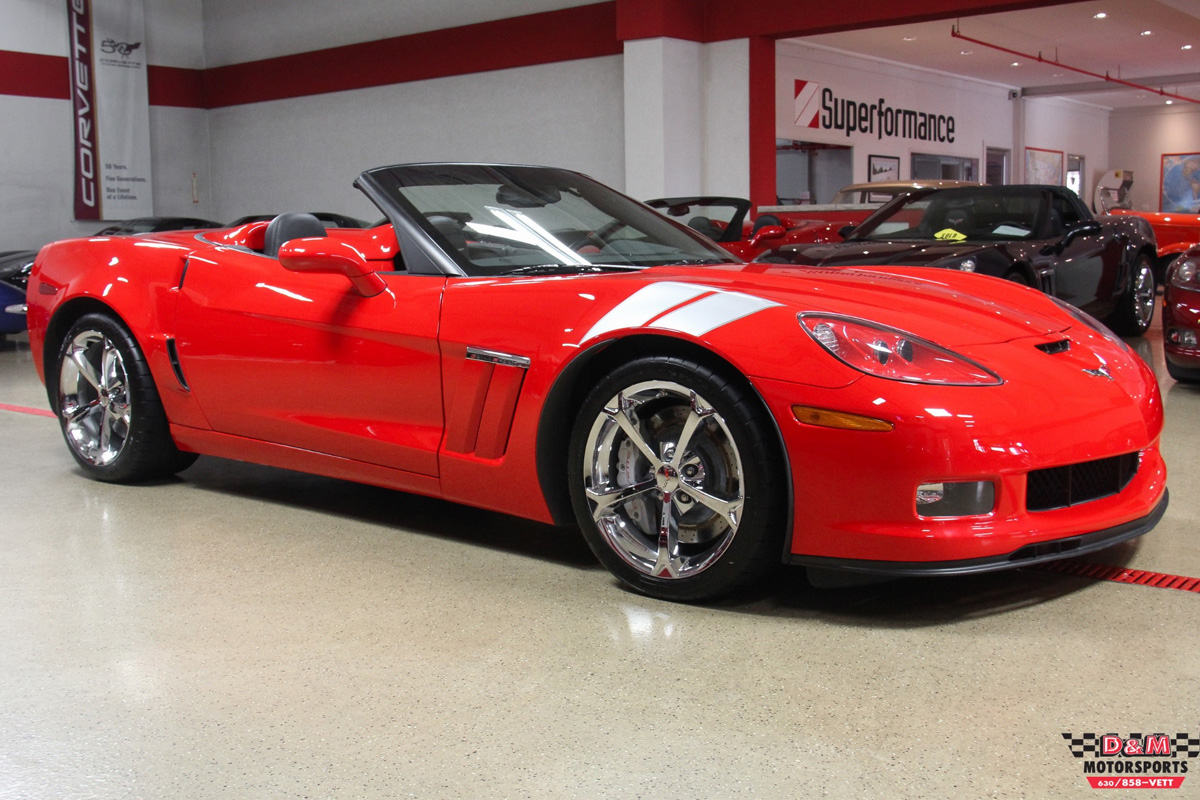

In 2010, Chevy not only continued its four Corvette lineup, but it also added a new model, the Grand Sport. The vehicle was unrelieved at a Corvette Birthday Bash in Bowling Green, Kentucky, at the National Corvette Museum. It used the LS3 power plant along with the Z06 Corvette’s wide track chassis and styling additions. It would be made available as a coupe or convertible. It would have higher performance than the base models plus sports suspension, more extensive trim, and an enhanced cooling system and brakes. All of the lineups came with a manual transmission option in the launch control system. In full-throttle launches, the system added performance upgrades to the standard stability system by adjusting engine speed to boost grip.
2011
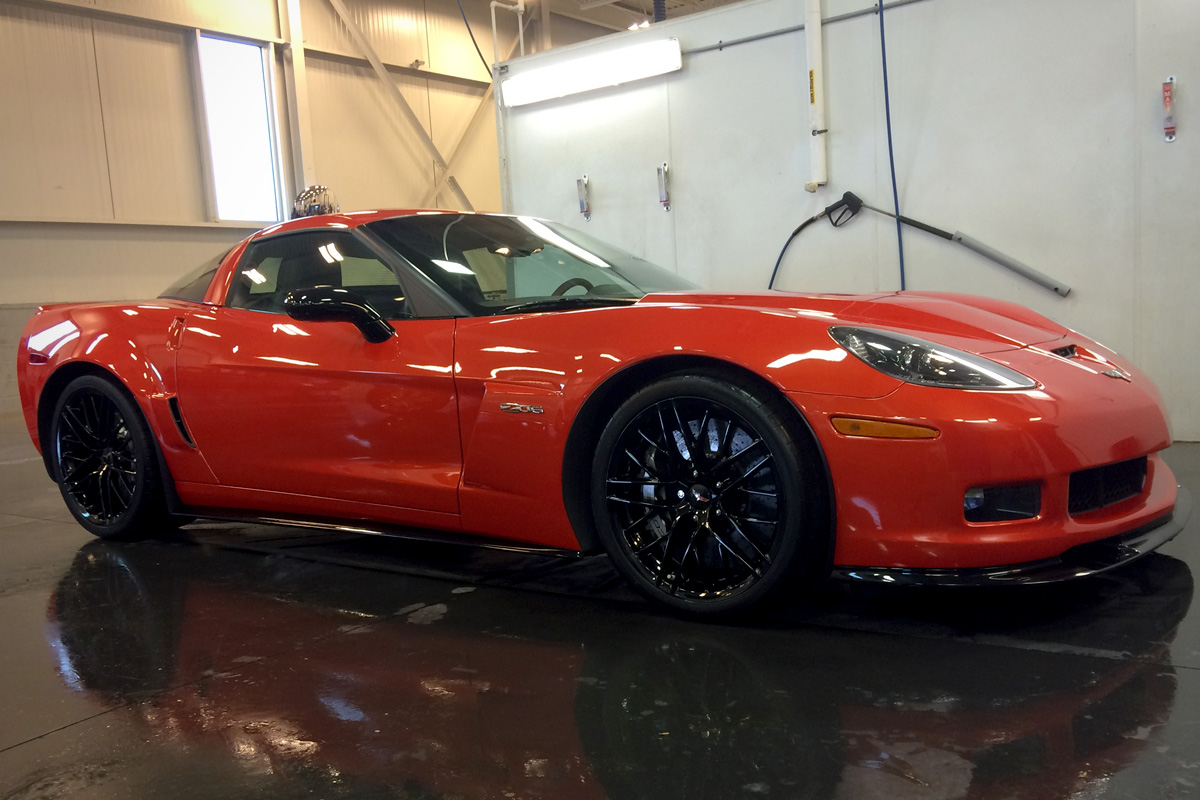

For the 2011 Corvette, Chevrolet added two new colors to the lineup: Inferno Orange and Supersonic Blue. With the base models, they received new five-spoke wheels. The wheels were competition style that came in silver, machine face, competition gray, and chrome. GM also sold RPO J55, a cross-drilled brake rotors option. As for the Grand Sport, a Chevy offered Magnetic Ride Control as an option that detects road surfaces and shifts damping rates. The most significant addition to this year’s Corvette was the two packages centered on the Z06: the RPO Z07 performance package and the RPO CFZ Carbon Fiber Package. The Z07 had Magnetic Selective Ride Control, ceramic brakes, Michelin Pilot Sport-2 tires, and 20-spoke wheels. The Carbon limited edition included carbon-fiber splitter, roof panel, rockers, and full-width rear spoiler. 2011 also saw an uptick in sales.
2012
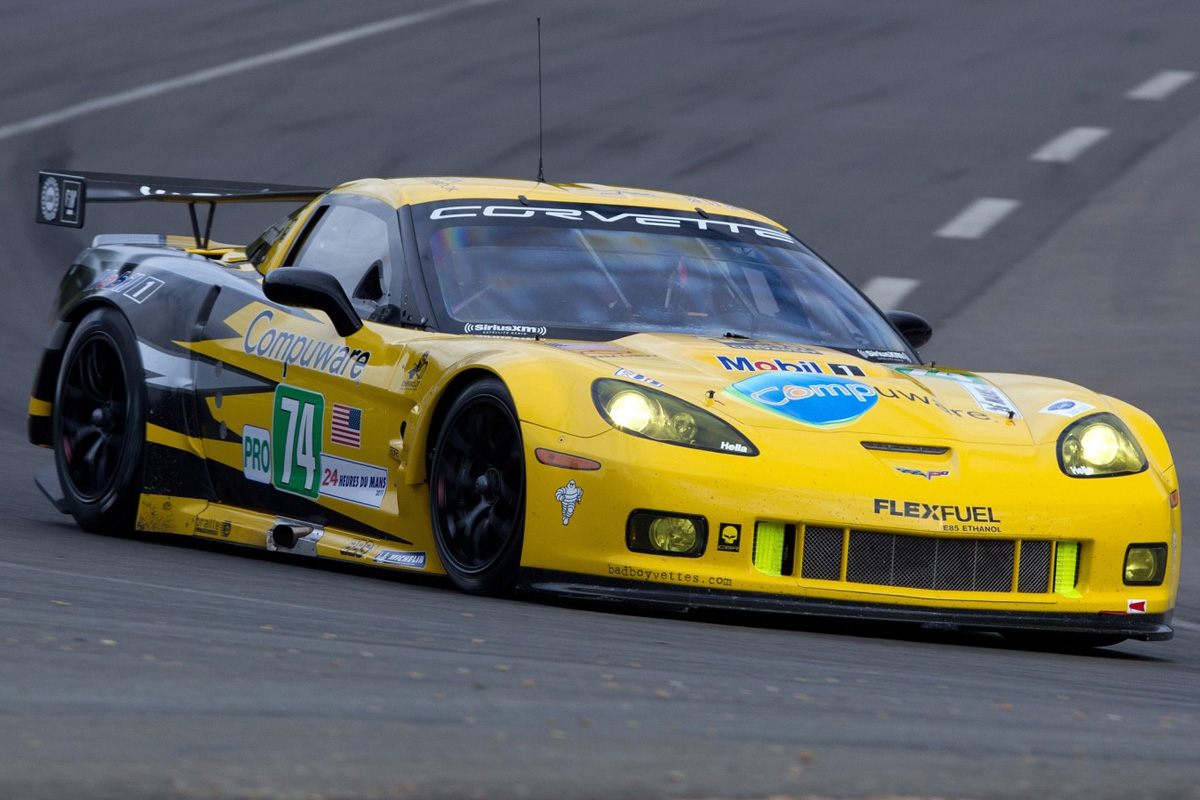

For 2012, Chevrolet showed off two new racing variants of the Corvette. These included the latest GT Contender and the Daytona Prototype class Corvette. As for the main lineup, many changes came to the interior due to criticism from earlier models. The main issue addressed was the seats. Customers and enthusiast levied comments for the lack of lateral support and adequate bolsters. Chevrolet’s new seats included a wider design, remolded back and headrests, and dynamic side-bolters. The goal for the seats was the driver would remain center at the steering wheel, even during races. Chevy also added a new steering wheel this year with updated switch trim and wrapped steering wheel spokes as well as model designations. Lastly, the company released a Centennial Edition. Unique to this edition was its Carbon Flash Metallic exterior with satin-black graphics.
2013
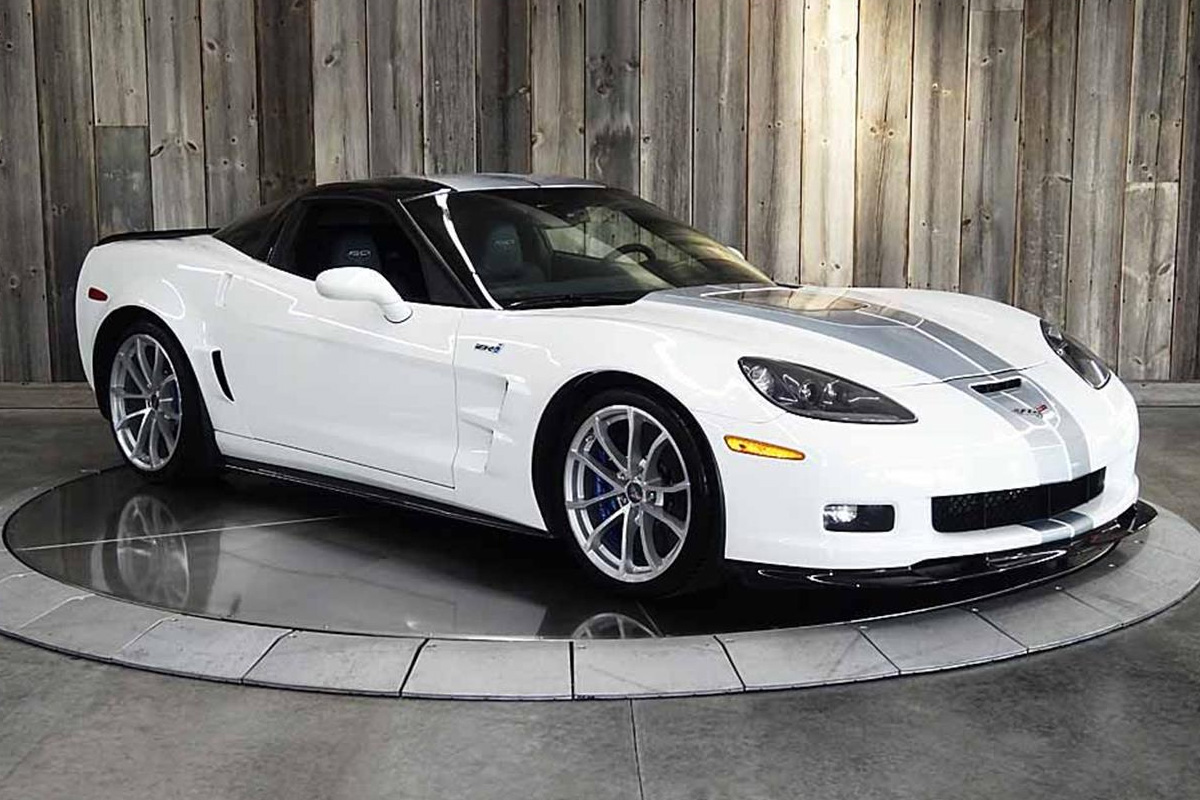

After nine years, the C6 was about to come to an end. In honor of the vehicle’s legacy, Chevrolet offered a 427 Convertible collector edition and a 60th Anniversary design package. The collector edition for the convertible combined traits of the Z06 and ZR1 including the LS7 Engine making it the fastest convertible Corvette in the company’s history. Looking at the design package, as seen in the picture, it came with an Arctic White finish, “60th” logo badging, and a blue diamond-wrapped interior. Production was cut short with the final 2013 model rolling off the Bowling Green Assembly plant on February 28 of that year. The purpose of discontinuation was for GM to shift focus on the production of seventh-generation Corvette looming around the corner.
2014
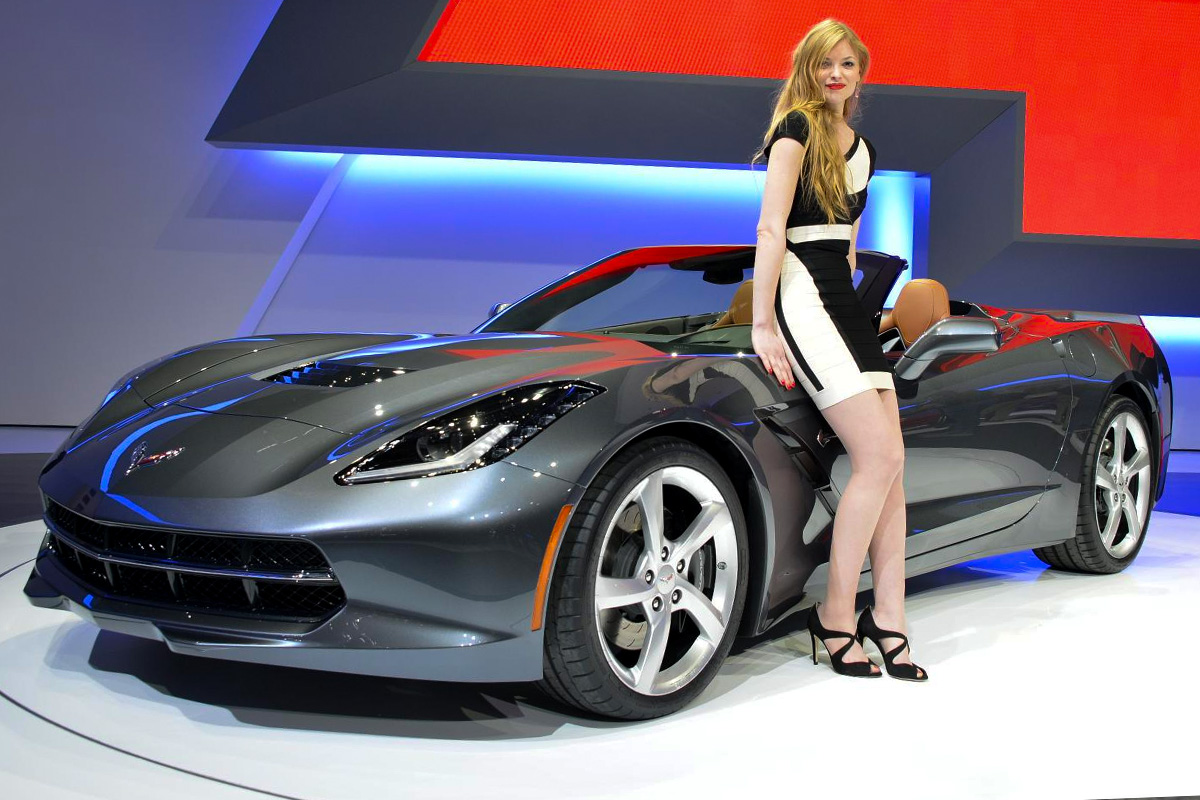

In 2013, the moment had come. Chevrolet unveiled its closely guarded next-generation Corvette at the Detroit Auto Show broadcast live on streaming platforms such as YouTube and Facebook. It was the 2014 C7 Chevy Corvette Stingray. Lead exterior designer Hwasup Lee and his team completed the vehicle’s design back and 2010 and 2011. Design director Kirk Bennion submitted the design in 2011 where the division’s design director Tom Peters approved it. The Stingray was constructed to take advantage of lightweight materials, electronics, and engineering advancements. It has a carbon fiber hood and rear led tail taillights. Like its predecessor, Chevy made its chassis from hydroformed aluminum. The vehicle also uses Aerogel to prevent heat from the transmission to travel into the cabin. The 2014 Corvette uses a 6.2-liter, LT1 V-8 engine with an impressive 450 horsepower rating. Stylistically, the vehicle is quite different from previous generations with more angular characteristics such as aerodynamic aids cut into every body panel. This angular design is especially apparent in the rear with the trapezoidal taillights. The lineup included a Coupe, Convertible, and Z51 Performance Package and Premiere editions. The Stingray was exceptionally well received, and at the North American International Auto Show, the Corvette was given the title “2014 North American Car of the Year.”
2015
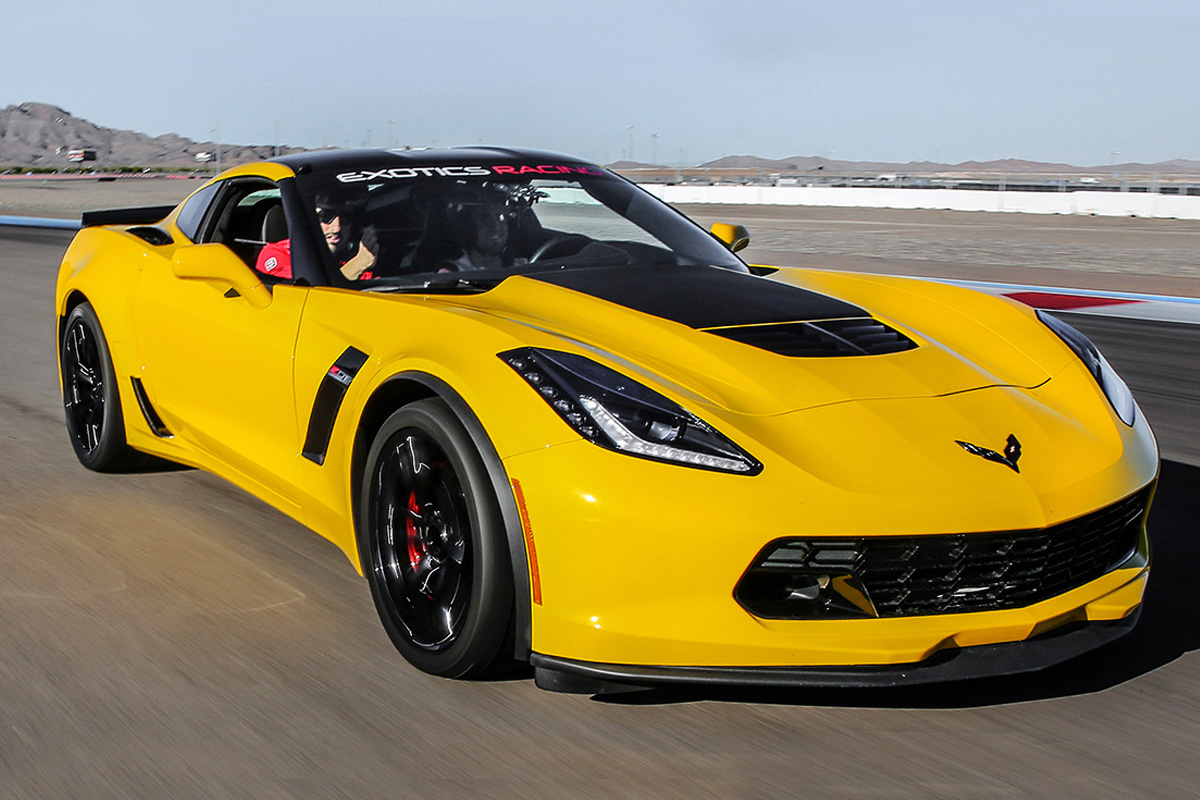

In 2015, Chevrolet made several upgrades to the Corvette. For one, all models came equipped with the 8L90 eight-speed automatic transmission. Also new were two new design packages: The Pacific Design Package and The Atlantic Design Package. Chevy offered the Pacific package with Z51-equipped coupes with at least a 2LT or 3LT trim levels. The Atlantic package, on the other hand, was provided with a Z51-equipped Stingray convertible. However, the most significant addition was the return of the Z06, which came with a supercharged and intercooled LT4 V8 engine that generated a whopping 650 hp. It now had removable carbon-fiber roof panels, carbon fiber hood, front fender vent, larger rear-fascia openings, Brembo brakes, etc. A Z07 package was offered, too, with a Michelin Pilot Sports Cup 2 P285/30ZR19 front and 335/25ZR20 rear tires.
2016
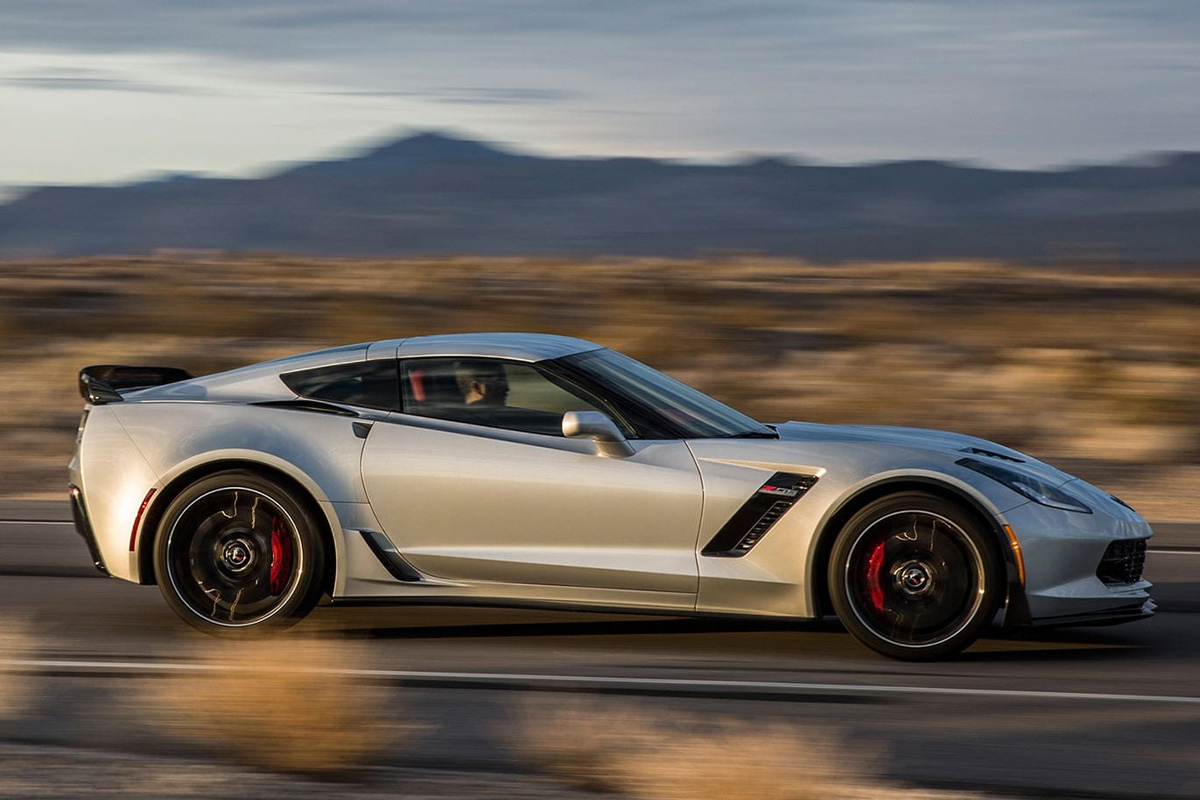

For the 2016 Corvette, Chevrolet included three color-themed design packages for 3LT and 3LZ trim models: Twilight Blue, Spice Red, and Jet Black Suede. They also offered a new Z06 C7.R Edition with a racing theme appearance and graphics. The new Vettes also came with a flat-bottom steering wheel designed so drivers have an instant feel to their directional input. Lastly, specific models received smartphone projection technology and front curb view parking cameras, which was an excellent addition to avoid obstructions. We should also note midway through the production year Chevy phased out four exterior colors.
2017
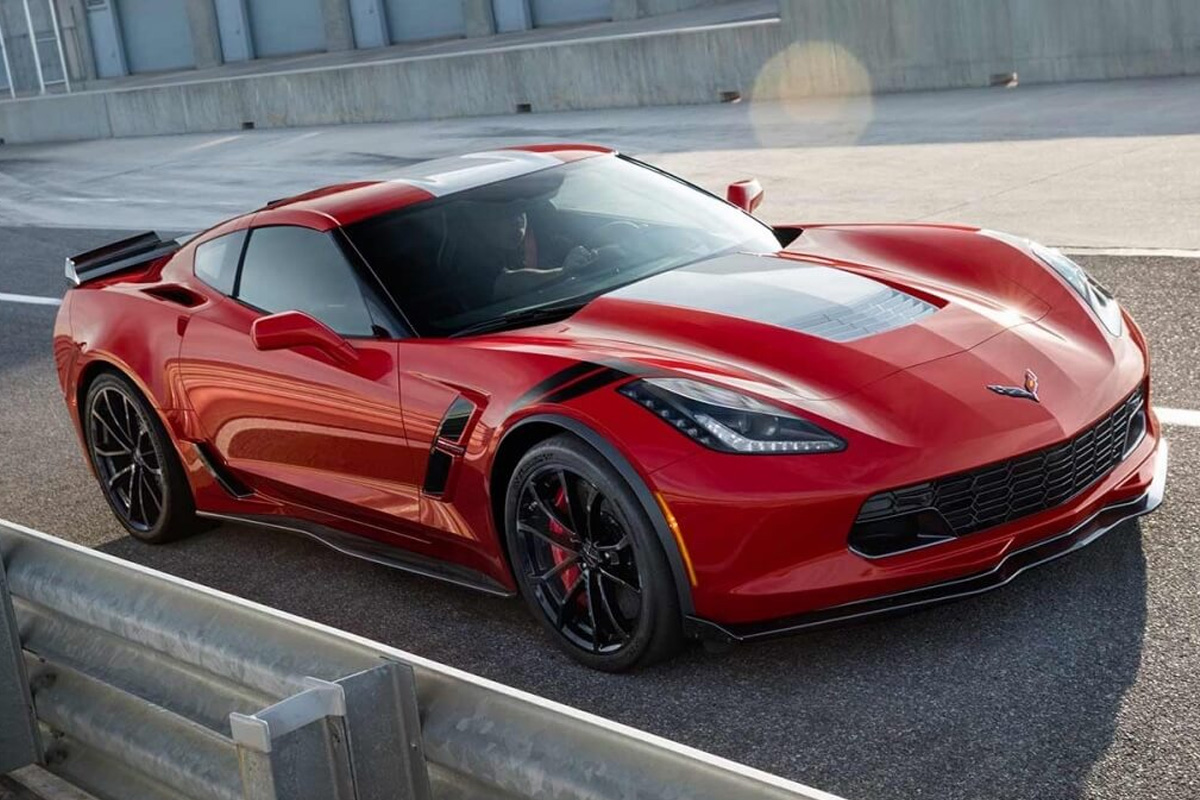

For most of the 2017 Corvette lineup, Chevrolet offered various packages with every model to allow customers to really customize their car to the way they want, including interior, exterior, and performance trims. Though, what Chevy wished to highlight was the triumphant reappearance of the Corvette Grand Sport. They revealed on March 1, 2016, at Geneva Auto Show. It had track-honed aerodynamics package, lightweight structure with an LT1 V8 engine rated at 460 hp. The car also came with a convertible or coupe option with a 7-speed manual or 8-speed automatic transmission. Along with the standard Grand Sport (Z15), Chevrolet sold, and Collector Edition (Z25).
2018
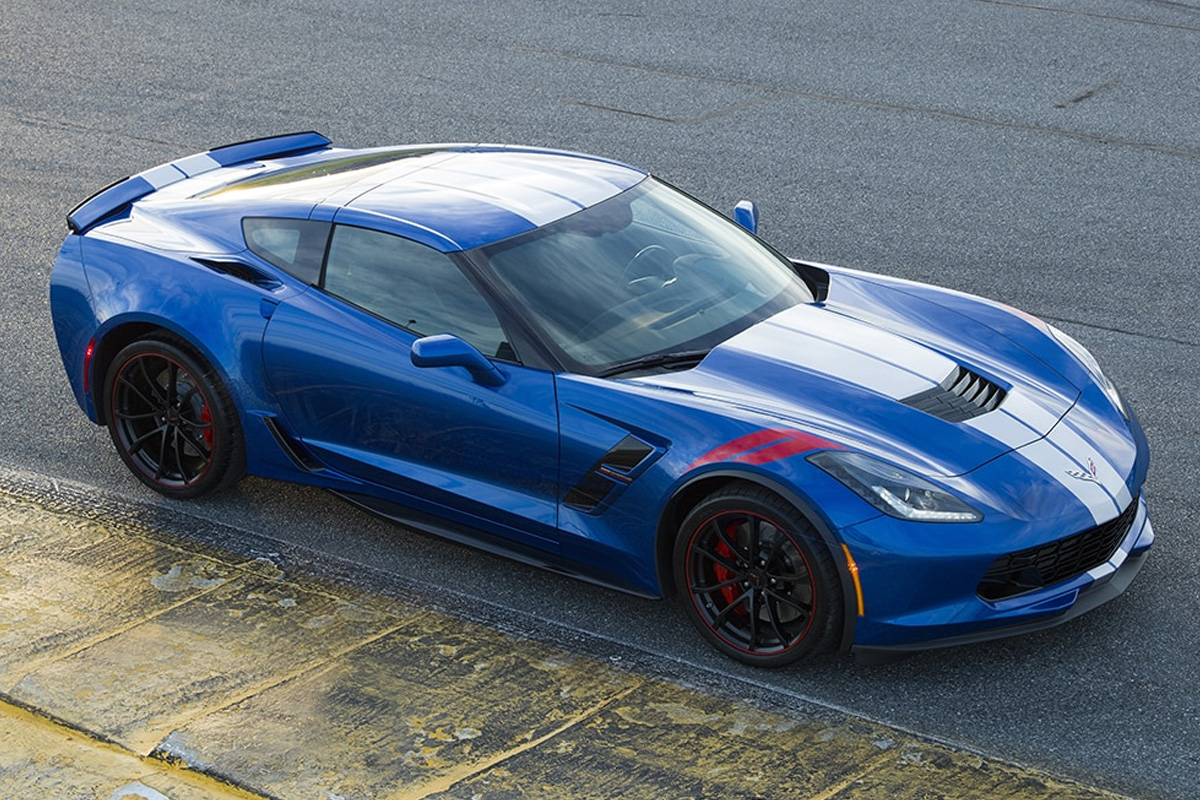

Chevrolet carried over the Stingray, Grand Sport and Z06 models for the 2018 lineup. Many of the trim packages offered from the previous model year carried over as well. The 2018 Corvette saw some minor changes, including HD Digital Radio as standard equipment, upgraded rear-view camera, the optional Performance Data Record added four new channels, and the Heads-Up Display received improved graphics. If you drove a Z06, you got a choice between two wheels. Corvette was also celebrating its 65th anniversary this year, so Chevy offered the Carbon 65 Edition (Z30). It came painted in Ceramic Matrix Gray with exclusive detailing. It was available on both the Grand Sport 3LT and Z06 3LZ.
2019
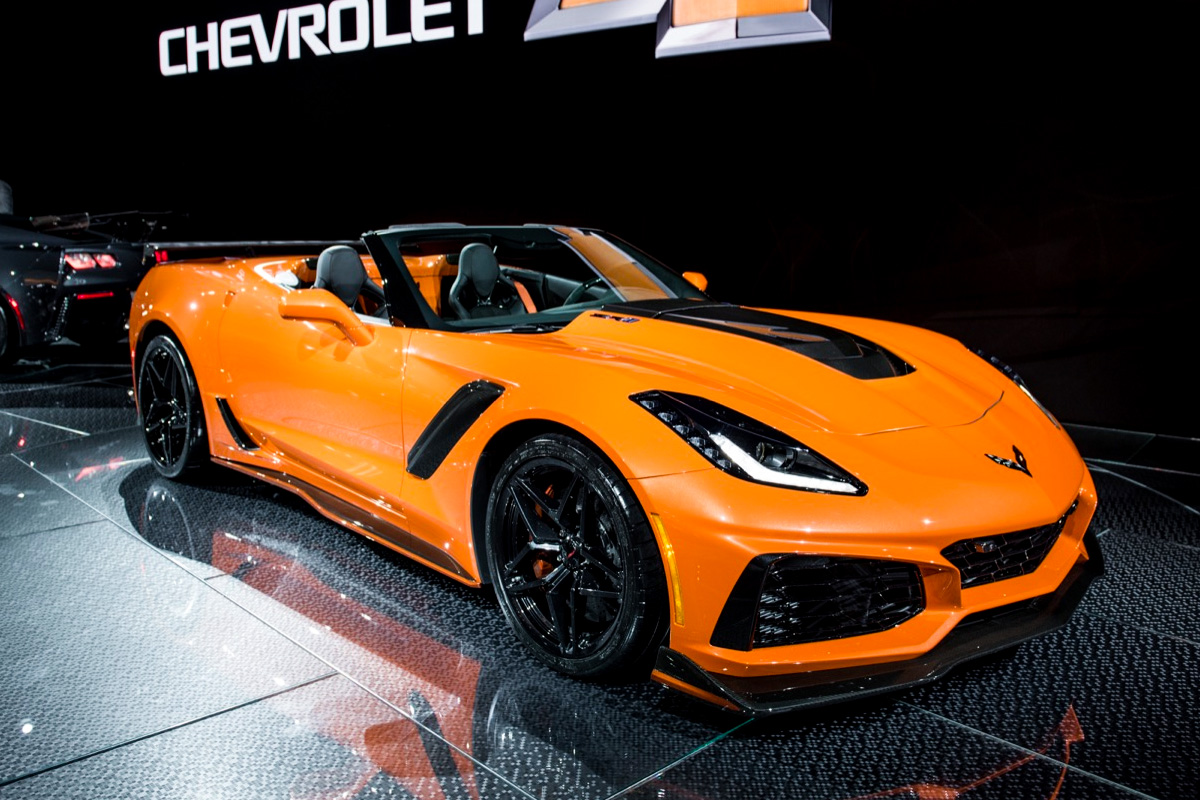

2019 was the last model year for the C7, and it went out with a bang. Chevrolet reintroduced the ZR1 built off the Z06 design. It came equipped with an LT5 V8 engine along with an Eaton supercharger rating the Engine around 755 hp. The vehicle also has an advanced engine cooling system. Along with the ZR1, Chevy announced a special edition of the Grand Sport called the Driver Series. The four paint schemes for these limited editions Corvettes were selected by drivers Oliver Gavin, Jan Magnussen, Antonio Garcia, and Tommy Milner.
2020
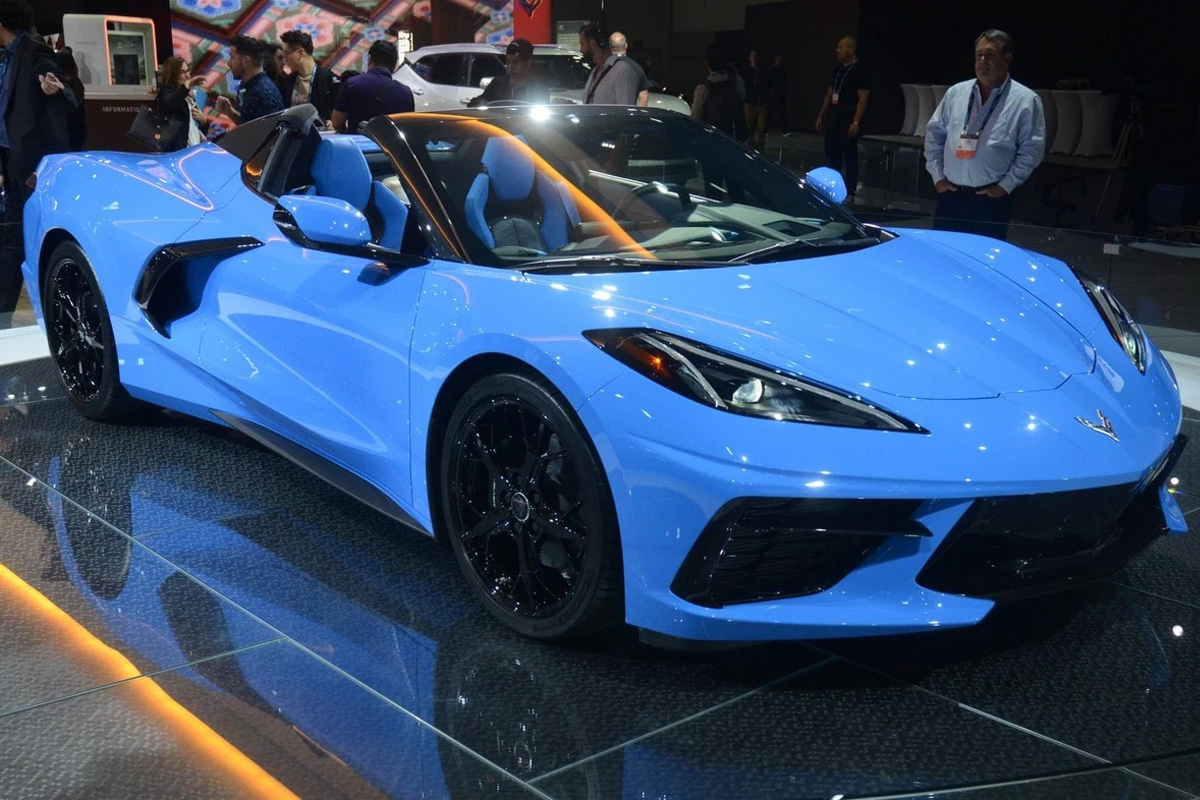

A new generation of Corvette has begun. The highly anticipated C8 was unveiled at the Kennedy Space Center July 18, 2019. It kept some design characteristics of the C7, but Chevy revamped the bulk of the exterior, putting massive attention on aerodynamics and cooling. You can see this with side scoops that contain air intakes. Chevrolet even put vents under the taillight. The C8 Stingray has a 6.2 L LT2 V8 engine with a 490 hp rating. It also has an 8-speed dual-clutch automated transmission manufactured by Tremee, an unequal length double wishbone suspension with monotube shock absorbers on all four wheels. Speaking of wheels, the Stingray utilizes alloy wheels with 19 inches in the front and 20 in at the rear with Michelin Pilot Sport ALS as the standard tires. New to the inside of the vehicle is a hexagonal steering wheel. A digital screen replaced the instrument cluster and a button on the wheel to activate custom performance settings. The Corvette C8 received the 2020 Motor Trend Car of the Year.
We look forward to seeing what Chevrolet has in mind for the coming Corvettes.